Welcome to the first “80/20 version” of a book ever written! Since most people are busy and do not want to take the time to read a full-length book, this is a condensed version of God’s Rainbow Connection: Fractal Code and Resurrection that contains about 20 printed pages of content and a list of approximately 450 references. It is based on the Pareto principle or 80/20 rule, which means that while it is less than 20% the length of a typical 300 page book (it actually is around 30 printed pages or 10%), it should have close to 80% of the value of the final version. This is especially true if someone is willing to follow all of the references, which often contain additional notes and link to external webpages or video clips.
If you want to quickly get a sense of what the book is about, it is recommended that you first go to the book section of the About page and read the few paragraphs there. In addition, there is a summary of the book which is much shorter than this webpage.
Contents:
- Introduction
- The Bible and Fractals
- Information Theory and Biology
- Conscious Emergence and Philosophy
- Information Trimonism: A Fractal Trinity
- New Observations and a Materialist’s Paradox
- From Turing Machines to Holographic Minds?
- Helping to Resurrect the Watchmaker Analogy
- DNA Repair and a Logical Loop of Feedback
- A Biological Jacob’s Ladder and a TOE?
- Control Engineering and the Bible
- References (with comments)
Introduction
The story of the book I am writing began when I got tired of the commercialism surrounding Christmas over twenty years ago and wondered if there was more to Christianity then what I had learned growing up as a Baptist missionary kid in the Congo and the Philippines. When I started researching the various modern traditions connected with the holiday season, I came across information on atheist websites which also talked about the amount of wasted matter, energy, and space in the universe as well as how evolution can be explained completely by chance. I had seen some of their arguments before, but I realized I had not really thought about objections to Christianity very much.
I decided I needed to become neutral (or agnostic) and do more studying in order to figure out if it was reasonable to believe in God in the first place, even though it made me feel like I had lost my best friend. At the time I was not familiar with a quote frequently attributed to Werner Heisenberg, a scientist who won the Nobel Prize for discovering the uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics. Heisenberg may (or may not) have said, “The first gulp from the glass of natural sciences will turn you into an atheist, but at the bottom of the glass God is waiting for you.”(1)
Despite any uncertainty surrounding the precise source of the quote, as I kept gulping knowledge I found out more and more about the fine-tuning of the universe. The most amazing example I learned of was the cosmological constant,(2) a force associated with dark energy and the increasing expansion of space which appears to be tuned to the astronomically small number of 10−120. This is equivalent to the size of half a grain of sand compared to the rest of the universe.(3) If this constant were a tiny bit stronger or weaker, all of the matter would have apparently rapidly expanded or collapsed shortly after the Big Bang, making life impossible. Several other finely-tuned constants(4)(5)(6) plus signs that the formation of the Moon (important to the development of life on Earth) was an extremely rare event(7) made it even more difficult to believe everything in the universe was a waste or the result of random accidents. On the other hand, Young Earth Creationism (YEC) and most of the ideas offered by the Intelligent Design movement seemed to be an incomplete “God of the gaps” story, so I kept studying.
The Bible and Fractals
One website discussing evidence for God from science also talked about how Passover reveals Jesus,(8) which surprised me because I thought it was a Jewish festival. So I learned how Jesus died at the exact time that the lamb was supposed to be killed each spring according to the Bible’s instructions written around a thousand years earlier. I also learned how Passover and the rest of the Holy Days(9) foreshadow seven literal spiritual days of Yeshua (Jesus’ name in Hebrew which means “God’s salvation”).
The sequence of the biblical Holy Days made more sense to me than modern traditions, and as I continued to study the Hebrew roots of Christianity I noticed other patterns of creation, separation, and restoration in the Torah (or instruction) seemed similar. This included the seven universal “days” of creation described in the beginning of the book of Genesis that are most commonly understood as representing ages or long periods of time.(10)(11) So I lined up all of the patterns in a table along with seven colors of light from the rainbow, the sign (or code) of the covenant promised to Noah and all living creatures by God. When I started showing it to a few people, one minister said the complex version of the table (which is located in the Appendix webpage and is called “A Fractal Periodic Table of ‘Elements’ of the Bible’s Light”) was the best one-page summary of the Bible he had seen.
As I was putting the table together I realized it was fractal, where each part has the same character as the whole but repeats at different scales. I already knew a little bit about fractal patterns and how they are found in math and nature, like tree trunks continually splitting into smaller and smaller branches, twigs, stems, and then smaller and smaller veins in leaves. Or rivers growing bigger and bigger through a system of streams and tributaries.(12)(13)(14) More research uncovered that a lot more things were fractal than I expected, such as electrons sometimes behaving in a way that looks like a fractal “butterfly.”(15) I even realized that rainbows are really a fractal “rainbow of rainbows” (see a diagram on the Summary webpage for details about how interfering light waves create faint supernumerary bands).(16)(17)
Incidentally, the timing of Jesus’ death, burial, and resurrection may also fit into a self-similar, repeating pattern that is known as a fractal. Although biblical scholars do not completely agree on the exact date, there is evidence that:
- He died in Hebrew year 3790 (30 AD), which is in the middle of the “week” of millenniums or 7,000 year period in the Bible that starts with Adam(18)
- He was cut off in the middle of the last “week” of years in a prophecy by Daniel which is interpreted as being 490 years long(19)
- He was crucified in the middle of the week on a Wednesday(20)
Fractals can also be found in technology such as cell phone antennas(21) or image compression,(22) in paintings by artists like Jackson Pollock,(23)(24) in aspects of logic,(25) and in cellular structures.(26) Fractal patterns are hidden everywhere in the biological language of life too, from how DNA physically folds into three-dimensional globs of globules,(27) to how parts of the genome are encoded,(28)(29)(30) and to how networks of cells signal and synchronize together.(31)(32)(33)(34)(35)
I also discovered a few Jewish(36)(37) and Christian(38)(39)(40) people were seeing other examples of fractal text patterns in the Bible, which is actually a book of books(41)(42) that explains how to operate in a fifth dimension of good and evil.(43) So I was not alone, and their work additionally helped me to realize that the Hebraic code of law consisting of 613 mitzvot or commandments in the Torah is essentially a more detailed fractal version of the Ten Commandments—which are in turn a more detailed fractal version of the Great Commandment to love God in addition to loving your neighbor as yourself.(44)(45)
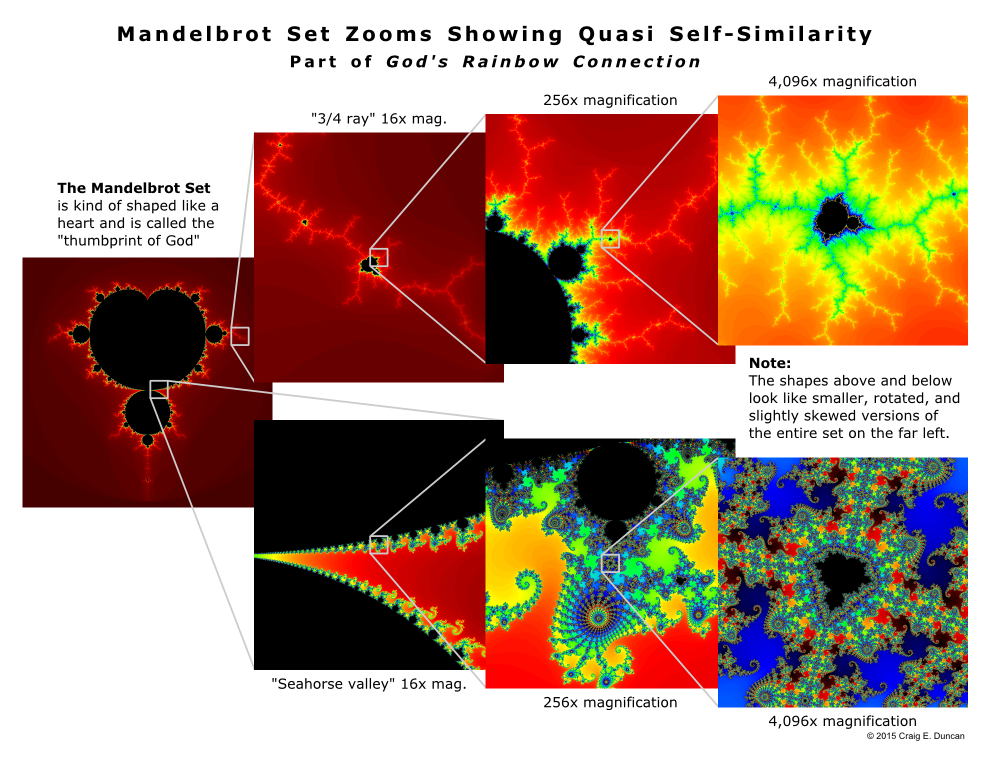
More importantly, I realized Yeshua was talking about God being fractal when He said, “I am the vine, you are the branches” almost two thousand years before the word was coined. It made sense a fractal God would be the best explanation for the emergence(46)(47)(48)(49) of a universe full of fractal patterns, including the famous Mandelbrot set which is composed of smaller connected fractals called Julia sets(50) and is known as the “thumbprint of God.” Interestingly, although the Mandelbrot Set is an infinitely complex two-dimensional slice of even higher-dimensional mathematics, it can be described with a simple formula (or code).(51)
Information Theory and Biology
Once I was aware there were multiple kinds of fractal patterns in the Bible, I decided to write a book to share this knowledge with other people. However, as I did even more research, I came across information theory and its relationship with codes (which are systems of rules connecting symbols and meaning that allow something to represent something else)(52) and consciousness. The existence of encoded “symbolic meaning” turned out to be the last gulp of science for me before the bottom of the glass in the quote attributed to Heisenberg. It made me happy because it confirmed that a belief in God is rational, although it is still not possible to use it to conclusively demonstrate the existence of God or even other minds with science.(53)
“Information is information, not matter or energy. No materialism which does not admit this can survive at the present day.”— Norbert Wiener, MIT Mathematician and father of cybernetics
For instance, according to an engineer, business consultant, and bestselling author named Perry Marshall—who is helping to popularize ideas from a German information theorist named Werner Gitt(54)(55) and symbiotically integrating(56) them with the latest discoveries in systems biology—all codes humans know the origin of (i.e., almost all of them) have come from a mind. No one has ever found an example of a digital code that has been verified to come from a purely material source, although Perry Marshall has created a prize potentially worth 10 million dollars to search for an exception.(57)(58) Until someone does, it is reasonable and logical to infer a 100 percent connection between consciousness and the emergence of the genetic code in DNA (where for example a sequence of three adenine or “A” nucleobases symbolically represents the amino acid lysine),(59)(60) which at this point is of unknown origin.
“The existence of a genome and the genetic code divides living organisms from non-living matter. There is nothing in the physico-chemical world that remotely resembles reactions being determined by a sequence and codes between sequences.”— Hubert Yockey, Physicist and information theorist
This type of logic is known as inductive reasoning(61)(62) and is often used in philosophical statements like the premise “all humans are mortal” (even if it only ends up being one part of a larger deductive syllogism).(63) It is also used to derive scientific phenomena like Isaac Newton’s law of universal gravitation from experimental observations.(64) In short, the science of information theory and what linguists refer to as the “Einstein gulf”(65)(66)(67)(68)(69)(70) plus the encoding/decoding table of the genetic code shows God almost certainly exists unless proven otherwise.(71)(72)(73)(74)(75)
“The Atheist’s Riddle: ‘Show me a language that does not come from a mind.’ It’s so simple any child can understand, but so complex no atheist can solve.”— Perry Marshall
However, instead of God using Intelligent Design to directly create every plant and animal six thousand years ago or relying only on random accidents to improve living things, science has recently demonstrated the cells themselves are actively trying to adapt and are creating,(76)(77) borrowing,(78) and merging(79) new biological information into their DNA. This conscious emergence of information by organisms seems to be much more interesting than the extreme positions many creationists and atheists take.(80)(81)
Conscious Emergence and Philosophy
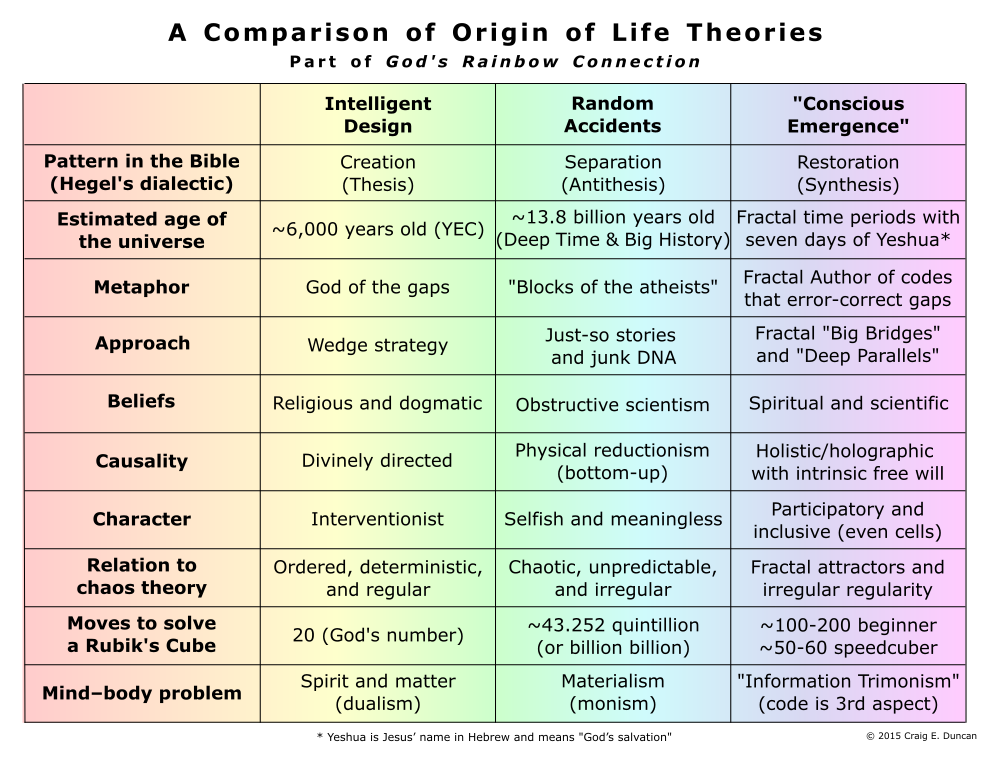
As a result, a new origin of life theory called “Conscious Emergence” is proposed in the book. It is a synthesis that resolves the tension between the thesis of Intelligent Design and the antithesis of random accidents, according to the three-stage Hegelian dialectic model in philosophy.(82)(83) To see a quick summary of information about it, please go to the “A Comparison of Origin of Life Theories” table located earlier in this webpage. Conscious Emergence is based on evidence of cellular agency(84)(85)(86)(87) and further develops ideas about the role of error correction in evolution by Alfred Russel Wallace, the often forgotten about co-discoverer of natural selection.(88) It also incorporates a version of natural theology proposed by Charles Babbage,(89) the “father of the computer.” This means it is a type of evolutionary creation(90) similar to the ideas promoted by Francis Collins, who wrote a book called the The Language of God and started the BioLogos Foundation.(91)
Conscious Emergence includes concepts like Natural Genetic Engineering (NGE)(92) by James Shapiro plus Denis Noble’s biological relativity(93) and harnessed stochasticity(94) (his name for adaptive mutation).(95)(96) It also includes multilevel/group selection(97)(98) and convergent evolution(99)(100) as championed by Simon Conway Morris, where contrary to the butterfly effect,(101)(102) the same basic forms keep showing up again and again in what the author calls a repeatable “flies to the butter” attractor effect.(103)(104) Most of this type of research has already been collectively described by others as “the third way of evolution,”(105)(106)(107) “Evolution 2.0,”(108)(109) or as part of an extended evolutionary synthesis.(110)(111)(112) It is additional evidence that we live in a participatory universe(113) with an information-theoretic origin as proposed by theoretical physicist John Wheeler,(114)(115) on top of the following scientific discoveries that Conscious Emergence is also based on:
- quantum delayed-choice experiments(116)(117)(118)
- cosmic microwave background anomalies(119)(120)(121)(122)
- problems with cosmic inflation(123)
- critical point scale symmetries (which are fractal)(124)
- quantum-critical biochemistry(125)(126)
- quantum tunneling in DNA repair(127)(128)
- patterns of punctuated equilibrium in the fossil record(129) and their similarity with the history of innovations by humans in areas like timekeeping(130) and aviation(131) (i.e., occasional large jumps in capability followed by long periods of no or only gradual improvements), which infers the presence of consciousness
Note: Conscious Emergence is a metalinguistic (meaning “beyond language”) theory of life’s origin that takes existing ideas in evolution like randomness, self-replication, and natural selection and combines them with additional principles based on recent discoveries by scientists. Some of these are the seeming appearance of retrocausality in quantum mechanics(132)(133) as well as unexpected connections between physics, information, and holography.(134)(135)(136)(137)(138)
There are also indications of cellular agency due to Lamarkian soft inheritance via epigenetic code,(139)(140) the creation of brand new orphan/ORFan genes,(141)(142) genetic redundancy where biological functions are buffered by multiple genes,(143)(144)(145)(146) and error correction of DNA. In fact, it turns out that before the “survival of the fittest” occurs, what has been termed as the “arrival of the fittest”(147) relies on mutations or adaptations which are not random across the genome,(148)(149) often do not come from changes in gene sequences,(150) and also depend on the “arrival of better fixes”. These are the increasingly complex and effective DNA repair mechanisms(151) that are highly genetically conserved themselves and reduce replication errors to less than one in a billion in humans.(152)
This continual improvement of the error-correcting systems encoded in DNA is an example of what the author calls the “principle of error minimization”—and it proves that there is more to evolution than just a bunch of random accidents followed by selection by the environment!(153) This principle is also found in several other areas of biology, such as the optimization of the genetic code against point mutations/mistranslation and how the brain minimizes prediction errors through a process known as predictive coding. These concepts are discussed in more detail later in the “DNA Repair and a Logical Loop of Feedback” section of this webpage.
Of course, rather than living organisms just acting as observers of Wheeler’s “it from bit,”(154)(155) there appears to be a fractal Author composed of many authors drafting and then lovingly editing and correcting gaps in the story via “code from wit”. In other words, instead of a universe from nothing(156) or from an old man with a beard in the sky,(157) there is a Suprapersonal Consciousness(158)(159) entangled with each person as they choose to conscientiously help order, goodness, and life emerge or allow themselves to slide into chaos, evil, and death. These indications of “creatio ex informatio”(160) in a distributed “panexintheistic” (meaning both “all because of God” and “all then God”) type of process theology(161)(162) led me to study a broad spectrum of scientific fields and philosophy from the perspective of information theory.
Especially key were significant insights about information by Robert Doyle, who describes himself as the “Information Philosopher.”(163) His insights include information’s value(164) in locally reducing entropy, which is commonly associated with disorder or uncertainty and is a measure of the number of ways something’s microscopic parts can be rearranged without changing its macroscopic condition.(165)(166) Robert Doyle also sees information as having a role in the solution to philosopher David Hume’s moral is–ought problem(167) and has come up with a two-stage model of free will.(168)(169)
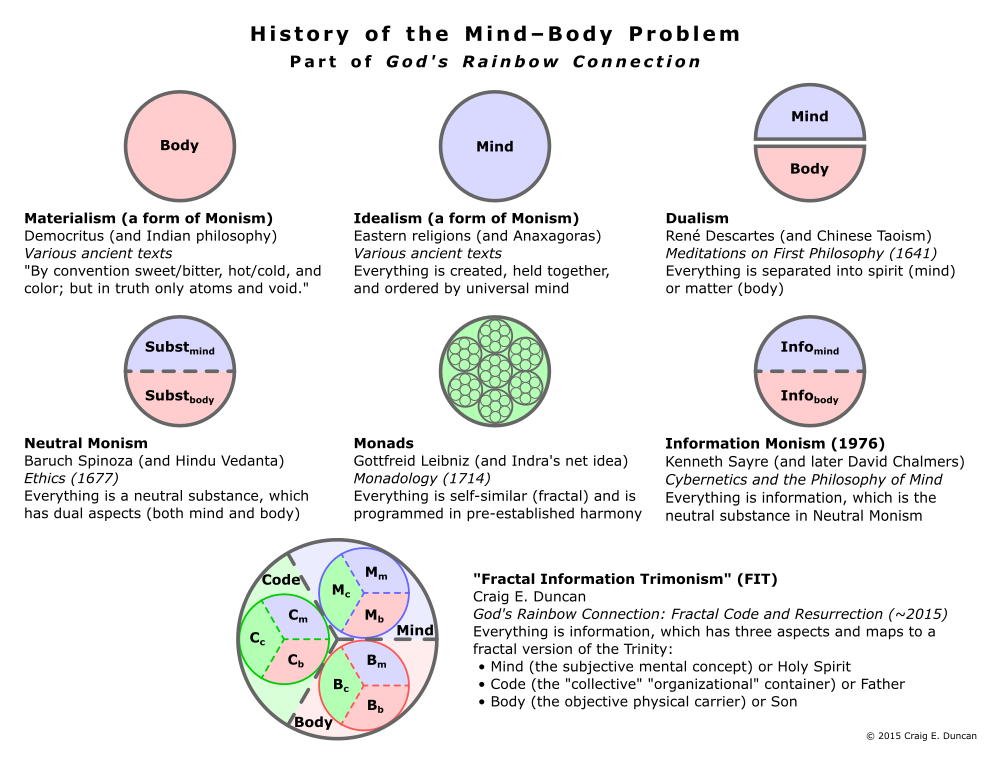
All of the research confirmed that while the universe has a material component, it also contains meaning symbolically encoded in information. This fact helped inspire me to develop a new holistic explanation of the mind–body problem that is fractal and contains a recursive type of “information about information” known as code. It appears to be a breakthrough that resolves the problem of interactionism (or what connects mind and body together),(170)(171) which has existed in modern Western philosophy since René Descartes’s formulation of dualism nearly four hundred years ago!(172)(173)
Information Trimonism: A Fractal Trinity
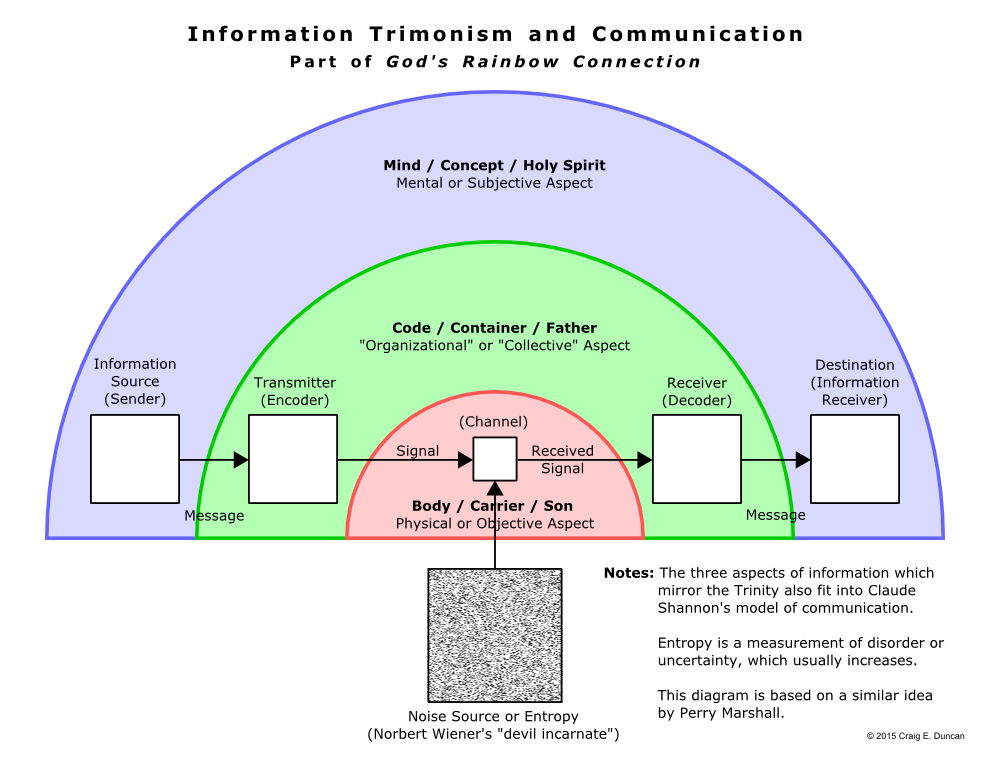
Similar to how Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity and the discovery of quantum mechanics extended classical physics, “Information Trimonism” extends the ideas of many philosophers (especially the classical rationalists),(174) as shown in the diagram above. It is based on the observation that “organizational” codes with symbols containing meaning such as those found in DNA are always present along with physical atoms/body as well as mental consciousness/mind in living beings. Information Trimonism links these three aspects of information with fractals (see a diagram on the Summary webpage for more details), the semiotic triangle(175)(176)(177) of language,(178) and the theological doctrine of God as an intertwined Trinity(179)(180)(181) in a way that can be considered aesthetically pleasing.(182) In addition, these aspects (which were described as attributes by Baruch Spinoza(183) and who only identified two of them(184)) of physical extension, a new “organizational communication” via code, and mental thought echo the data, information, and knowledge hierarchy of information science plus the subjects of grammar, rhetoric, and logic in the liberal arts. In short, Information Trimonism is a fractal triple-aspect monism.
Information Trimonism can be thought of as a fractal twist of the linguistic turn in philosophy (which was originally developed by Ludwig Wittgenstein and others)(185) that is based on information theory(186)(187)(188) and with a third aspect of code acting as a container or language conduit.(189) Or it can alternatively be seen as a version of Karl Popper’s three worlds(190) (or mathematician Roger Penrose’s slightly different one)(191) involving self-similar patterns of syntax, semantics, and a type of pragmatics emphasizing the differing emotions generated by the context of a message.(192) This means that Information Trimonism describes the weaving together of a suprapersonal, personal, and intrapersonal holarchy(193) of objective reality, “collective” codes, and the subjective feelings which individuals create relative to their beliefs about the other two.
“The whole of philosophy in this way resembles a circle of circles. The Idea appears in each single circle, but, at the same time, the whole Idea is constituted by the system of these peculiar phases, and each is a necessary member of the organisation.”— G. W. F. Hegel in his Encyclopedia of the Philosophical Sciences (1817)(194)
(Incidentally, a modern Information Trimonism-based interpretation of this quote would be: “Instead of turtles all the way down,(195) it is information all the way around.”)(196)
Information Trimonism also adds a middle “layer” of code or mental representation(197) which actually consists of multiple fractally-distributed sets of code (somewhat comparable to a hidden layer of nodes in an artificial neural network)(198) to the thesis of multiple realizability originally formulated by Hilary Putnam.(199) This architecture allows the same mental state to theoretically have different physical implementations,(200) as long as the code is adjusted to compensate. The fact that the code contains symbolic meaning also helps to explain why a theory of intentionality (the observation that mental states are about or of something else)(201)(202)(203) is associated with the mind.
The fractal nature of Information Trimonism additionally supports one of Putnam’s arguments for semantic externalism,(204) where he points out a linguistic community is necessary in order to help an individual person make meaning. Since multiple sets of code coordinate the interaction between mind and body, including the correction of errors, Information Trimonism also echoes aspects of Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz’s theory of pre-established harmony(205) with programmed monads which are fractal.(206) The distributed character of the code sets (in addition to the fact that code symbolically refers to something else) also offers a way to help bridge the problem of “Leibniz’s gap”(207) that exists between mental perceptions and physical mechanisms.
The relationships between the aspects of Information Trimonism are interdependent:
- body = code + mind (from quantum delayed-choice experiments)
- code = mind + body (from knowledge of how humans formulate languages)
- mind = body + code (from scientific observations of living creatures)
So Information Trimonism may provide clues as to why we have subjective experiences known as qualia. Incidentally, this question of why cognition is accompanied by experience has recently been reformulated as the “hard problem of consciousness” by philosopher David Chalmers.(208)(209) The nature of qualia has also been discussed in a “What Is It Like to Be a Bat?” paper(210) by Thomas Nagel (who has additionally written about natural teleology)(211) as well as the knowledge argument or “Mary’s room” thought experiment(212) by Frank Jackson. Even if Information Trimonism is unable to offer any insights into subjective experiences, its fractal nature can be combined with ideas like:
- the Integrated Information Theory (IIT)(213) of consciousness proposed by Giulio Tononi
- the CIP Framework(214) by Federico Faggin
- Value Realism(215) by David Rousseau
- the Somatic Marker Hypothesis(216) by Antonio Damasio that suggests emotions guide behavior
New Observations and a Materialist’s Paradox
Information Trimonism can also be the basis for brand new observations. One example of the three aspects of Information Trimonism that may be familiar to people involves a social construct known as money.(217) In the case of a coin, at the physical level, it objectively has a third side known as the edge which is normally overlooked but connects its obverse (heads) and reverse (tails) sides, similar to how biological codes sit between mind and body. A coin also carries stamped codes containing information important to a collective group of people, and it actually has three separate conceptual values. These range from a mentally subjective market value, to an encoded legal value (which can vary greatly from the subjective market value if the coin is rare or if high inflation is occuring), and to the intrinsic or melt value of the physical metal.
Interestingly, someone starting with little or no money who is informed they are now “worth a million dollars” will almost certainly react differently than a person who originally had a billion dollars—even though both of them currently have exactly the same amount of money. This resembles what occurs when fans of opposing sports teams have very different subjective feelings after a scoring play (like a goal in soccer), although they both collectively agree about the meaning encoded by the sport’s rules into the objective event of a ball crossing a line. Information Trimonism can be applied to other far-ranging examples such as the model of events, beliefs, and emotions in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), the science of music, and even the mathematical theory of all communication created in the 1940s by Claude Shannon.(218)
Taking my new philosophical model of Information Trimonism and using what I had learned about information theory, I also realized any statement claiming only material things exist also carries symbolically encoded meaning. This results in a “materialist’s paradox” similar to the paradox in Kurt Gödel’s incompleteness theorem in mathematics.(219)(220) It is also related to the symbol grounding problem(221)—and even if someone is eventually able to prove a digital code can originate naturally, it will still hold true.
In addition, the non-physical meaning of the statement causes different subjective feelings (pro or con) in other people’s minds about what is being claimed depending on their current worldview, showing pure materialism to be false on multiple levels. To put it another way, while a person is not entitled to create their own private version of what a statement means, they are completely free to have their own individual feelings about the collectively agreed upon meaning. So when it comes to information, code and emotions matter just as much as matter.
From Turing Machines to Holographic Minds?
Like the philosophical theory of machine-state functionalism(222) by Hilary Putnam, the three aspects of Information Trimonism can be superficially compared to the elements associated with a Turing machine. This idealized model of all computation consists of a physical read/write head with storage tape, an instruction table containing code, and a state register that tracks the current step of a calculation in a quasi-mindlike fashion. The comparison can then be recursively applied to just the code because variable assignment statements, function pointer dereferencing (which allows computer code to be dynamically linked), and self-modifying reflective metaprogramming in some modern programming languages outwardly follow the same three-fold pattern of increasing virtualization. This triple progression can also be seen in the instantiated objects, interfaces (which encode information about code), and abstract classes of object-oriented programming. It additionally applies to the physical, logical, and high-level conceptual models used when planning enterprise information systems architecture.
However, as the philosopher John Searle has argued when discussing whether artificial intelligence (AI) is conscious, a computer simulation of a fire does not burn things like an actual fire.(223) This is similar to how there is no symbol grounding or understanding of the meaning of the language being processed in his Chinese room thought experiment.(224) (Although a case could be made that the Chinese symbols may be grounded with very different meaning in Searle’s mind by his understanding of their relationship to the program’s instructions.) So the overall comparison with computers breaks down at the conscious level, because only the external human circuit designers, coders, and application users currently appear to be mentally “a-ware” of the meaning of the results generated by the layers of hardware and software. As mentioned earlier, the existence of this consciousness or qualia in humans and other organisms is a fundamentally hard problem to explain and it seems to be based on more than just processing raw data with algorithms.(225)
Problems related to consciousness in philosophy:
Name Question Solution Mind–body What is the connection? Code in fractal patterns Symbol grounding How is meaning understood? Maybe holographic? Hard problem (qualia) Why is there feeling? Maybe fundamental?
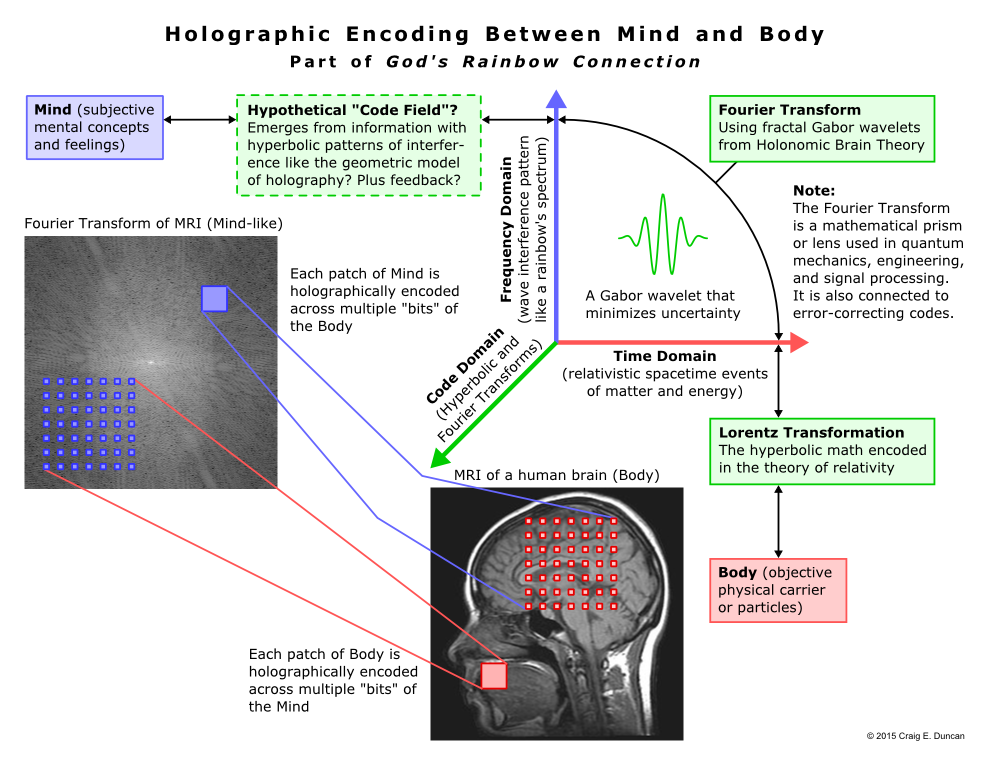
Instead, the biological computation(226)(227) and embodied cognition(228) associated with consciousness might be something like a holographic(229)(230) version of Plato’s Cave(231)(232) involving a “code field” which is conceived as being analogous to a five-dimensional light field.(233) Each part of the underlying physical architecture that potentially gives rise to this hypothetical code field could contain fractal and ergodic (which is a technical term for irregular regularity or statistically similar)(234) patterns of information about the whole,(235)(236)(237)(238) similar to the Buddhist idea of Indra’s net.(239)(240)
The “surface” of these patterns of “information in formation” would appear to be random like the speckle patterns in holographic film,(241) the messages transmitted by certain error-correcting codes,(242) streams of bits in stochastic computing,(243)(244) and even weights between layers of nodes in AI.(245)(246) Incidentally, these four examples run counter to Richard Dawkins’s claim about life being “complicated things that give the appearance of having been designed for a purpose,” because they show there are things with random patterns that may (or may not) subjectively appear to be complicated—even though they are actually a result of purposeful design.
However, the “cross section” of this code field of information would appear to have interference fringes (similar to the supernumerary bands found in rainbows which were discussed earlier) that are arranged in nested hyperbolic lines of flux like the geometric model of holography.(247) This could create the logical equivalent of a flat map with virtual symbols which seem to pop up into three-dimensional space.(248) Somewhat similar to a newly discovered 2.5-dimensional mixing of surface and bulk states in graphite,(249) the shape of these symbols and therefore their relative linguistic meaning could shift depending on the perspective or mental interpretation they are observed with,(250)(251) while a deeper-rooted sense of self would still remain stable.(252)
“
Spacetime tells matter[Mind tells information] how to move;matter tells spacetime[information tells mind] how to curve.”— A quote by theoretical physicist John Wheeler summarizing Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity that has been modified so it applies to consciousness
This might be due to a conjunction of quantum(253)(254)(255)(256)(257) and classical error correction(258) (or even a new kind based on a type of quasiparticle called a skyrmion)(259) providing feedback similar to a thermostat, centrifugal governor,(260) or windmill fantail.(261) (Incidentally, although governors and fantails are not digital, they contain parts which mechanically symbolize/represent something else and generate an emergent non-physical control law described mathematically by a transfer function.)(262) In addition, the code field would be arranged in a way that allows the complex holographic logic in the brain(263)(264)(265)(266)(267) emerging from this theoretical matrix of information to have some kind of cybernetic(268) control over itself and the ability to choose how to adapt(269)(270) and modify its underlying physical structure by rewiring it.(271)(272) It would represent a mind capable of self-organization(273) or in other words, a case of mind over matter.(274)
Helping to Resurrect the Watchmaker Analogy
While developing the idea of Information Trimonism, I also realized that significantly improving a recent improvement of the watchmaker analogy by Perry Marshall would make it a valid teleological argument(275) after all, at least until someone finds a natural digital code. This analogy is associated with William Paley(276) but actually dates back more than two thousand years to the time of Cicero, a Roman statesman, orator, and writer.(277) Regardless, Perry Marshall has made an important breakthrough by being the first person I am aware of to identify that the element common to both watches and life is language(278)—although he has not been the only one to do so since then.(279)
“When you see a sundial or a water-clock, you see that it tells the time by design and not by chance. How then can you imagine that the universe as a whole is devoid of purpose and intelligence, when it embraces everything, including these artifacts themselves and their artificers?”— Cicero, De Natura Deorum, II.34 (45 BC)
However, Perry Marshall’s claim about the language being present in a missing external blueprint or which exists as an idea in someone’s mind before a watch is built can not be proven. In other words, he has not identified the correct location of the language at all. What needs to be taken into account instead is the objective encoding of information occurring inside of a watch after it is wound up (which then winds up being displayed on its face) plus the presence of error-correcting mechanisms!
To be more specific, a watch measures physical movement via a controller(280) and encodes the discrete pulses on an indicator(281) such as a clock face or digital display for humans to read, in a much lesser version of how a cell uses language with symbols and meaning which has to be translated.(282)(283) So the information (which symbolically represents something else) in watches has actually been staring us right in the face all along. To be fair, this fact has probably been missed because people have only been aware of the presence of information in biology since 1965 when Francis Crick confirmed the existence of protein-coding sequences in DNA(284)(285) that can be detected through Fourier analysis.(286) This ability to create and/or utilize information similar to living organisms shows that measuring instruments like timepieces are not just collections of mechanical parts arranged in patterns which can subjectively appear to some people like William Dembski to have specified complexity.(287)
In fact, the difference between information containing encoded symbolic meaning which causes(288) top-down(289)(290) real effects(291)(292) and objects that only have complicated physical features is analogous to the way an image and a randomly scrambled version of itself have completely different Fourier transforms (although the histograms measuring their pixel brightness will be exactly the same).(293) This is because in general, the magnitude part (which does not have any phase information) of an image’s Fourier transform will have a central blur with lines radiating out from it and/or a circular halo surrounding it, while a transform obtained from scrambled pixels will look darker and grayer but still be random like the static “snow” on a television set.(294) A typical magnitude part of a non-random image’s Fourier transform can be seen above in the “Holographic Encoding Between Mind and Body” diagram.
“There cannot be a language more universal and more simple, more free from errors and from obscurities, that is to say more worthy to express the invariable relations of natural things.”— Joseph Fourier on mathematics in his book The Analytical Theory of Heat (1878)
There is a reason why these patterns of rays and cloudy arcs emerge in the Fourier transform of most images. Since a two-dimensional picture of something like a railroad track receding into the distance is affected by the requirements of railway engineering as well as the rules of three-dimensional perspective, the spatial arrangement of certain pixels is not entirely random and this gets represented in its Fourier transform. Along the same lines, it is possible to use the Fourier transform to prove an electronic clock signal with regular square wave pulses is not random because it results in frequency components that appear to make a wave of waves.(295) In contrast, the transform of a completely random white noise signal (which looks like an irregular zig-zag)(296) will just create another irregular zig-zag.
The existence of these hidden, underlying relationships between the various parts of images and signals that have non-random Fourier transforms helps to explain why information can also cause powerful feelings. An example of this would be a person who looks at their watch and realizes that the relationship between the long and short hands and the numbers they are pointing to means they are running late to an event they want to be on time for, resulting in them becoming upset and to start rushing to get there. This is in contrast to someone seeing a device displaying a bunch of random shapes or dots that have no relationship to anything, which typically will not generate much of an emotional response because they have no meaning to humans—even if they seem to look more complex.
As mentioned earlier, in addition to encoding information, watches have a built-in feedback mechanism (which is a harmonic oscillator that keeps vibrating at a resonant frequency)(297) to correct errors so time can be represented with a code more accurately. Cells in living organisms also require some type of error correction since they constantly need to fix their genetic information because of damage from random events and diseases. This allows them to stay alive and keep on performing important functions such as locally reducing entropy(298)(299)(300) and replicating their DNA.(301)
“What’s not random is the cell’s response to the threat. Damage is random. Repair is not.”— Perry Marshall
Incidentally, Perry Marshall has pointed out the DNA repair systems found in the cells of living organisms are not random but purposeful,(302)(303) which counters criticisms by David Hume and others.(304) It also contrasts with a statement by evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins about how “the universe we observe has precisely the properties we should expect if there is, at bottom, no design, no purpose, no evil and no good, nothing but blind, pitiless indifference.”(305) Perhaps Dawkins is not aware of control engineering principles and the existence of error-correcting systems which use code and logic to detect mistakes and repair information that has become corrupted by noise,(306)(307)(308) especially those in biology.
Even artificial life simulations running genetic algorithms which attempt to show that evolution is random make use of error correction, which is ironic. It turns out that computer engineers have designed many different ways to fix errors which are hidden throughout the computers in stock parts like redundant logic gates, hard drive reliability software, and high-end error correction code (ECC) memory modules. These never seem to be accounted for by researchers for some reason.
DNA Repair and a Logical Loop of Feedback
The various DNA repair systems found in cells actually form a vital and interdependent relationship with the encoded instructions they not only rely on but also protect. This creates an emergent low-level “logical loop” of feedback which provides the stability necessary for the development of life. Other people have come to the same conclusion about the ability of biological systems to correct genetic errors as well,(309)(310) based on research started in the 1970s due to the inherent instability of DNA molecules. The still ongoing research has revealed the existence of multiple repair mechanisms (including one which relies on quantum tunneling and demonstrates an indirect link between the laws of physics and the genetic code),(311)(312) resulting in three scientists recently winning a Nobel Prize.(313)(314)(315) Since RNA is less stable than DNA,(316) even if the RNA world hypothesis of life’s origin is possible—and it may not be(317)—some kind of error correction has always been necessary. In fact, if “nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution,”(318) then “nothing in evolution makes sense except in the light of control engineering.”
Requirements of the logical loop of feedback:
- Parts need code to carry and represent logic
- Code needs logic to control and replicate parts
- Logic needs parts to correct and repair code
This means that not only does evolution depend on the self-replication of cellular parts,(319)(320)(321) which depends on code,(322)(323)(324)(325) but it also depends on non-random error correction(326)(327)(328)(329)(330) and mathematical principles (e.g., logical comparisons like XOR—which suprisingly has a fractal aspect identical to a certain type of Fourier transform).(331) These increasingly complex DNA repair systems(332) operate at a much deeper level and are more significant than the mere presence of complicated physical features proposed by some people like Michael Behe to have irreducible complexity.(333)(334) If anything in biology is irreducibly complex, it is actually the threefold relationship between the mechanical parts, the code with symbolic meaning, and the logic embedded in the error-correcting enzymes that appear to have all worked together in a feedback loop from the very beginning to make life possible. These are known scientifically as the proteome, genome, and regulome.
A comparison of terms from Intelligent Design (ID) and Conscious Emergence (CE):
Old ID terms describing complicated physical features (subjective) New CE terms describing symbolically encoded information (objective) Specified complexity “Symbolic meaning” Irreducible complexity “Logical loop”
This hypothesis is falsifiable (and therefore is scientific)(335) if someone can find a living organism which does not have any coded information or DNA repair systems, or is still able to evolve after one or both of them have been completely removed in the laboratory.(336)(337) Until then, DNA repair systems as well as the proofreading and editing of incorrectly charged transfer RNAs(338)(339)(340) in the biological translation process are further evidence that life is not a series of random accidents and the purely materialistic just-so stories told by some scientists are not true.(341)(342)(343)(344) In fact, evolution happens faster than what would be expected from chance alone.(345)(346)(347)(348) So continuing to tell these incorrect stories now is a form of what theoretical physicist Richard Feynman calls cargo cult science(349)(350) and is comparable to attempting to peddle a perpetual motion machine after a hidden energy source (or error correction in this case) has been revealed.
“If it could be demonstrated that any
complex organ[feedback loop with parts, code, and logic] existed, which could not possibly have been formed by numerous, successive, slight modifications, my theory would absolutelybreak down[be revealed to only be one part of a larger system].”— A quote by Charles Darwin in his book On the Origin of Species (1859) that has been modified to reflect the recent scientific discovery of DNA repair systems
Even worse, the stories have unfortunately acted like “blocks of the atheists.” This is because atheist’s claims about life basically being a bunch of blocks bumping around randomly actually go far beyond the views of Charles Darwin(351)(352) and have blocked or at least slowed down a lot of scientific progress in evolutionary biology. (To be fair, this also tends to happen when people on the other side of the spectrum retreat to “God of the gaps” arguments.) This “obstructive scientism” is only recently starting to be chipped away, such as when studies like the still ongoing ENCODE project(353) proved that most of the so-called “junk DNA”(354)(355)(356)(357) is actually functional and regulates the protein-coding genes.(358)
Incidentally, the ENCODE results help to explain why genome size is not correlated with the complexity of an organism, known as the C-value enigma.(359) It also means that the genomes of different species are kind of like different versions of a Rubik’s Cube solution guide, where the vast majority of information is about when biological systems should make a move or correction rather than describing the move itself. In other words, junk DNA (now often called non-coding DNA) is similar to the bulk of the instructions written in regular English text along with images showing how the Rubik’s Cube should look at each stage, while the rare protein-coding genes are equivalent to an occasional sequence of moves compactly encoded in Singmaster notation.(360)
Not only do the biological systems regulated by this non-coding DNA handle many types of errors in cells, but they are unexpectedly flexible—sometimes literally. For example, DNA base pairs have the ability to dissipate electromagnetic radiation(361) as well as flip and skew their orientation to absorb physical damage.(362) As far as the genetic code, several studies indicate it is optimized or fine-tuned on the order of one in a million in terms of error minimization,(363)(364)(365)(366)(367) although others suggest this redundancy is balanced with adaptability and the ability to carry parallel codes.(368)(369)(370)
“Much more than even physics, control is a mathematically oriented science. Control principles are always expressed in mathematical form and are potentially applicable to any concrete situation.”— Rudolf E. Kálmán, inventor of a filter or algorithm used widely in control engineering
Networks of neurons in the brain also use a “principle of error minimization” in the form of feedback loops(371) to make decisions in what is known as predictive coding,(372)(373)(374) active inference,(375) or free energy minimization.(376)(377) This is essentially an information theory version of the principle of least action in physics(378)(379) that was introduced by neuroscientist Karl Friston(380) and uses Bayesian inference to minimize prediction error (it also resembles Kalman filtering in engineering(381) or backpropagation in artificial neural networks).(382) However, intelligence additionally seems to involve what the author calls a “principle of choice maximization,” as demonstrated in simulated systems that are programed to move toward configurations that maximize their ability to respond to further changes.(383) This means it may be possible to quantify the real effects or causal efficacy of biological information(384) and therefore its value by determining its efficiency at locally reducing entropy and minimizing errors while simultaneously maximizing choices.
A Biological Jacob’s Ladder and a TOE?
In general, biological information relies on control nodes acting non-randomly in systems such as gene regulatory networks.(385)(386)(387) So instead of only being subject to the laws of physics, life is also governed by layers of non-physical mathematical control laws such as the logical loop of feedback formed by DNA repair systems as discussed in the last section. In fact, the continual improvement of these DNA error-correcting mechanisms in increasingly complex life forms is proof that there is an additional principle of error minimization involved in evolution beyond natural selection by the environment.(388)
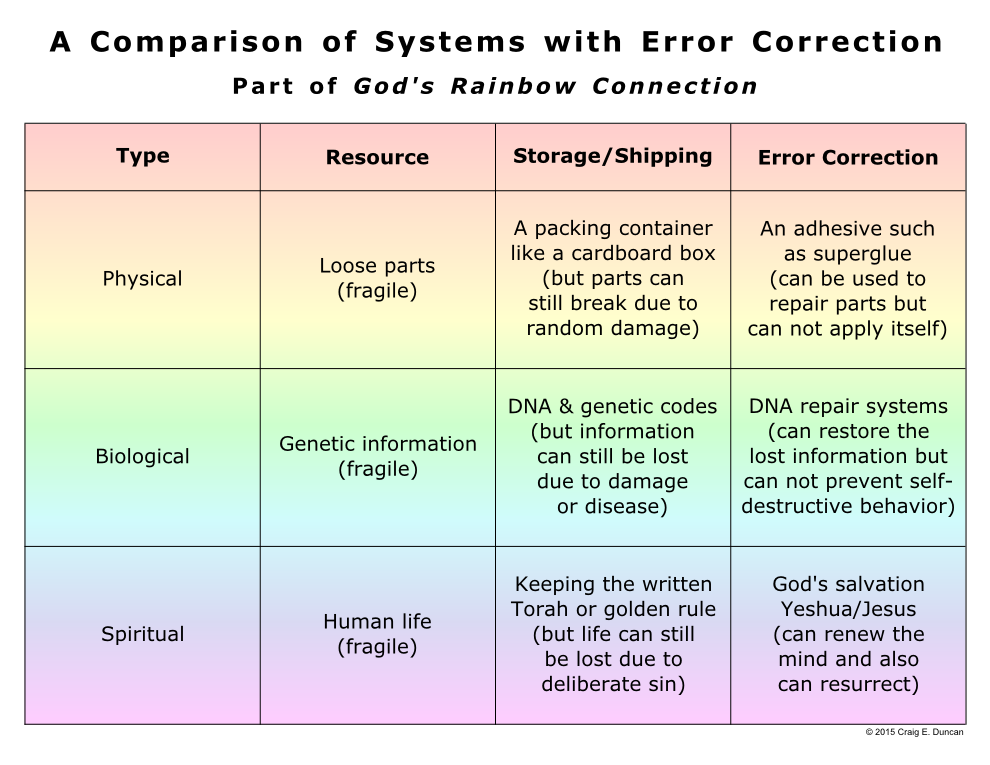
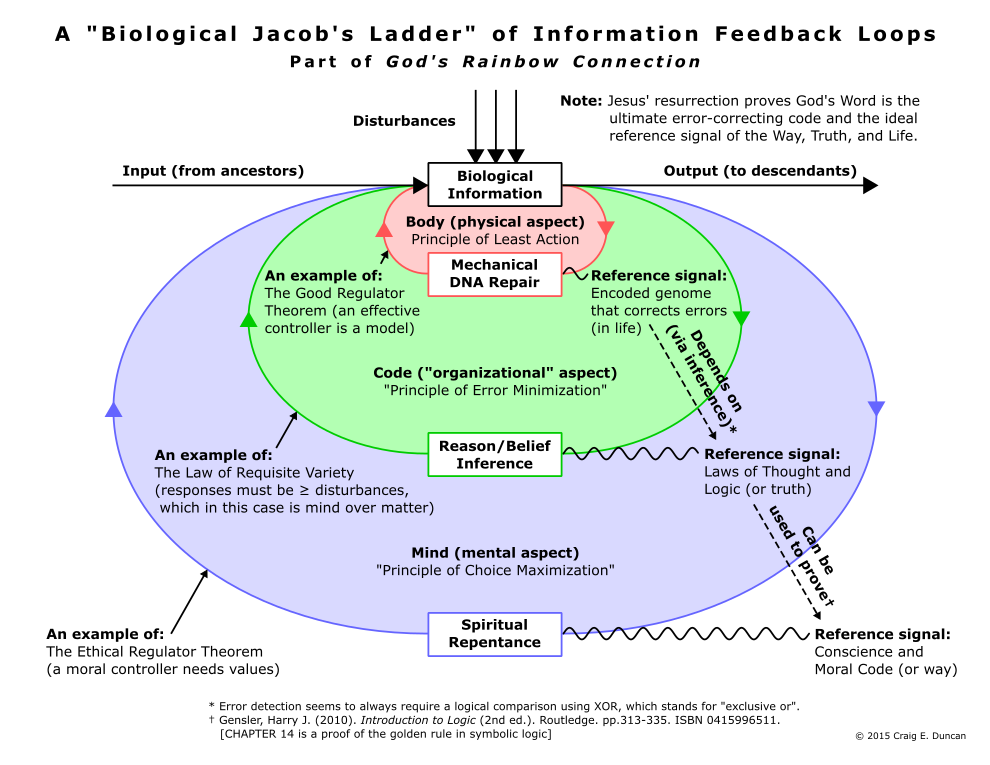
Multiple aspects of this error correction can be described with theorems(389)(390) by cyberneticians like W. Ross Ashby,(391) including the human desire to be ethical(392) and have the character to do the right thing morally(393)—even at a personal cost (in other words, have love).(394)(395)(396) This is because minimizing certain errors in behavior such as selfishness seems to maximize other people’s ability to make choices, since groups made up of altruistic individuals outperform groups of selfish individuals.(397)(398) So these control principles appear to indirectly connect the physical, mental, and spiritual realms(399)(400) of life (that are also discussed in the “A Comparison of Systems With Error Correction” table located earlier in this webpage) like a “Biological Jacob’s Ladder,”(401)(402) which is shown in the diagram below. This is similar to second-order cybernetics,(403) the practopoietic theory(404)(405) of system organization by Danko Nikolić, the idea of a level-crossing strange loop(406) by Douglas Hofstadter, and even the idea of possible second-order representations in mirror neurons which lead to self-awareness.(407)
The Biological Jacob’s Ladder demonstrates how disturbances to physical things in the body, which follow the principle of least action, can be overcome by code following a principle of error minimization. This can also be helped by mind choosing to reject selfishness and behave in a manner that follows a principle of choice maximization for other people, similar to how German philosopher Immanuel Kant (another classical rationalist) based morality on the preservation and promotion of rationality and rational agents.(408)(409) Due to the algorithmically beautiful way the information encoded in DNA contains the logical instructions to physically repair itself(410)—and the fact that logic can be used to prove the Golden Rule(411) (which is a type of altruism)(412)—the Biological Jacob’s Ladder also shows how Plato’s transcendental properties of beauty, truth, and goodness(413)(414) exist in a system of harmonius unity that is a key part of creating the great chain of being.(415) In addition, it links together the three traditional branches of philosophical inquiry! This was divided by the ancient Greeks around the time of Plato into physics, logic, and ethics.(416)
This breakthrough is somewhat like the unification of theories in modern physics,(417) such as various Grand Unified Theories (GUTs) where the electromagnetic, weak, and strong forces are theoretically merged into a single force.(418) The Biological Jacob’s Ladder could even be an intermediate step (or perhaps just a “toe-hold”) toward a holistic version of a Theory of Everything (TOE)(419) in Systems Philosophy,(420) which is known as a General Systems Theory (GST).(421)(422) For instance, it can be used to further help develop Robert Doyle’s information-based solution(423) to the is–ought problem and the related fact–value distinction,(424) resulting in the concept that “choosing to maximize information structures which maximize choice (by minimizing errors(425) and locally reducing entropy) is good.”
“Two things fill the mind with ever new and increasing admiration and awe, the more often and steadily we reflect upon them: the starry heavens above me and the moral law within me. . . . I see them before me and connect them immediately with the consciousness of my existence.”— Immanuel Kant, a German philosopher who believed that reason was the source of morality
Also, the Biological Jacob’s Ladder is recursive and fractal since it applies to entire human societies in addition to each individual. For example, scientists and engineers can use logic (which itself has fractal aspects)(426) and machines governed by feedback to help develop cures for diseases,(427) including those caused by physical damage to DNA like cancer. Then spiritual leaders can use universal moral truths like the Golden Rule(428) to create a just community(429) where as many people as possible are able to access these life-saving medical treatments. Perry Marshall calls this type of progress “Evolution Omega” instead of “Evolution Alpha” (which is simply another name for his cellular agency-based Evolution 2.0).(430) It is similar to Pierre Teilhard de Chardin’s biblically-inspired vision of all creation being pulled towards a state of divine unification called the Omega Point(431)(432) or the concept of an evolutionary “Fractal Ladder” by Bruce Lipton.(433) See “The Fractal ‘Big Bridges’ Theory” and “The Emergence of a Fractal Body of Christ” diagrams on the Summary webpage for depictions of different aspects of the Omega Point idea.
Control Engineering and the Bible
The Biological Jacob’s Ladder above also demonstrates the unreasonable effectiveness of control engineering principles in theology, similar to “the unreasonable effectiveness of mathematics in the natural sciences.”(434)(435) To be more specific, “nothing in Christianity makes sense except in the light of control engineering,”(436) which is similar to its importance in evolution as discussed earlier. This is because rather than being divided into non-overlapping magisteria or separate domains as paleontologist Stephen Jay Gould has suggested,(437) there are actually “deep parallels” between the science of abstract formal systems(438) and revealed Christian theology.(439) For example, due to the principle of error minimization, it can be shown for the first time ever that there is a link (although it is an indirect one) between the intelligence found in the universe and the God of Christianity. This is a paradigm shift similiar to what physicist and philosopher Thomas Kuhn says happens in scientific revolutions.(440)
Christianity is also not based on pseudoscientific arguments like scientists such as astronomer Carl Sagan claim.(441) Instead, God is using what are essentially control engineering techniques to try and minimize the grave consequences of non-existence (or death) due to self-inflicted data corruption (or sin).(442)(443) He does this by offering an invaluable(444) moral error-correcting code in multiple formats which operates at the highest level of consciousness and life.(445)
So on top of intentionally repetitive fractal written instructions, God sent a living version of the holographic Message(446)(447)(448) of salvation in the physical form of Jesus(449) who said, “if you love Me, keep My commandments” (which symbolize if someone is a good person) as well as “love one another as I have loved you.” However, religious leaders did not understand and decided to destroy the Message instead of delivering it. After a timeout of three days, this error was corrected because God retransmitted the Message by raising Yeshua from the dead, demonstrating that His recovery system works and proving His Word is true.
“ ‘It means,’ said Aslan, ‘that though the Witch knew the Deep Magic, there is a magic deeper still which she did not know.’ ”— From C.S. Lewis’s book The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe (1950)(450)
Despite doubts about miracles by David Hume,(451) this did not have to violate any of the laws of nature,(452)(453)(454) just like the error-correcting systems found in biology and telecommunications which can physically restore information by using a reference signal(455)(456) or code. In fact, the way parts of the physical world can be purposefully corrected with logic is a window to a much deeper Truth.(457)(458) One way to visualize this is with a hologram of a statue of Jesus. If the top part of the hologram where the head appears to be is cut off and hidden (a metaphor for crucifying the real Jesus), it is still possible to tilt the remaining broken “body of Christ” piece and see the head,(459) although it will be a bit fuzzier.(460) It is also possible to re-create the top part of the hologram from what is left using mathematical algorithms.(461)(462) The body can be observed in the top part too, similar to how Yeshua said, “anyone who has seen Me has seen the Father.”
“I believe in Christianity as I believe that the Sun has risen, not only because I see it but because by it, I see everything else.”— C.S. Lewis in his essay “Is Theology Poetry?” from the book The Weight of Glory (1949)
In addition to acting as a sign,(463) Jesus’ death, burial, and resurrection also functioned as a controlled burn(464) against sin and behaved like an antifuse,(465)(466) creating a way for humans made in the image of God to have life more abundantly.(467) Later, God amplified the recovered Message at Pentecost after encoding it into a virtual format (sort of similar to a spiritual email)(468) that could be downloaded and integrated into people’s lives more easily.
Sadly, other religious leaders interfered again with the transmission of the Message by adding noise to the signal in the form of inaccurate translations in the Bible such as “hell” instead of the original Hebrew word “sheol”(469) as well as modern traditions like a now hyper-commercialized Christmas.(470) Fortunately, because the written word of God is fractal and redundant, a lot of people including myself have still learned information about Yeshua during the holidays of Easter and Christmas—even though they are only partially based on God’s appointed Holy Days which more and more Christians are beginning to become aware of and observe. It appears the ultimate error-correcting Message is in the process of being completely restored a second time in order to connect those who decide to love God and each other (see some text and a diagram on the God’s Selfie webpage for more about this).(471)(472) In the meantime, I hope the book I am writing helps to explain some of what God is doing so more people choose to be part of it.(473)
“As the heavens are higher than the earth, so are my ways higher than your ways and my thoughts than your thoughts. . . . [S]o is my word that goes out from my mouth: It will not return to me empty, but will accomplish what I desire and achieve the purpose for which I sent it.”— Isaiah 55:9–11
^^^ Click here to go to the top of the page ^^^
References (with comments)
z
- Wikiquote contributors. “Werner Heisenberg – Wikiquote.” [Misattributed section. Note that a similar statement was made by Francis Bacon] en.wikiquote.org
- MrEpistemologist1’s channel. “(The Cosmological Constant) Leonard Susskind – YouTube.” [2:50 min long video with host Sir Martin Rees, from a TV series episode called What We Still Don’t Know: “Are We Real?”] www.youtube.com
- Santi Tafarella. “The Grain of Sand Argument for God’s Existence.” santitafarella.wordpress.com
- Richard Deem. “The Universe: Evidence for Its Fine Tuning.” web.archive.org (archived from the original at www.godandscience.org)
- drcraigvideos’ channel. “The Fine-Tuning of the Universe – YouTube.” [6:22 min long video created by philosopher and theologian Dr. William Lane Craig’s Reasonable Faith organization, see from the beginning to 3:44 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Cold-Case Christianity – J. Warner & Jimmy Wallace’s channel. “Three Illustrations That Demonstrate the Degree to Which the Universe is Fine Tuned – YouTube.” [8:58 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Rare Earth hypothesis – Wikipedia.” [A large moon section] en.wikipedia.org
- Richard Deem. “How the Passover Reveals Jesus Christ.” web.archive.org (archived from the original at www.godandscience.org)
- John Parsons. “A Concise Overview of the Seven Feasts of Israel.” www.hebrew4christians.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Allegorical interpretations of Genesis – Wikipedia.” [Contemporary Christian considerations section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Framework interpretation (Genesis) – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Fractal – Wikipedia.” [Natural phenomena with fractal features section] en.wikipedia.org
- BBC Ideas’ channel. “How fractals can help you understand the universe | BBC Ideas – YouTube.” [3:09 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Northern Diaries’ channel. “Is God A Mathematician? – Fractal Geometry of Nature – YouTube.” [6:59 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Hofstadter’s butterfly – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Les Cowley. “Supernumerary Rainbows.” www.atoptics.co.uk
- Wikipedia contributors. “Rainbow – Wikipedia.” [Supernumerary rainbows section. Note that “the very existence of supernumerary rainbows was historically a first indication of the wave nature of light, and the first explanation was provided by Thomas Young in 1804.” Incidentally, he did this by performing the predecessor of the famous double-slit experiment, which helped lead to the development of quantum mechanics] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Crucifixion of Jesus – Wikipedia.” [Chronology section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Prophecy of Seventy Weeks – Wikipedia.” [Christological readings section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Chronology of Jesus – Wikipedia.” [Scholarly debate on the hour, day, and year of death section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Fractal antenna – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Fractal compression – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Jackson Pollock – Wikipedia.” [Fractal computer analysis section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Fractal art – Wikipedia.” [Types section. Note that “perhaps the best example of fractal expressionism is found in Jackson Pollock’s dripped patterns”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Logical conjunction – Wikipedia.” [Definition section. Note the diagram on the right which is labeled “Conjunctions of the arguments on the left — The true bits form a Sierpinski triangle.” This is a fractal pattern, and similar ones occur in the truth tables of the other variadic Boolean functions] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Fractal – Wikipedia.” [Fractals in cell biology section] en.wikipedia.org
- Ed Yong. “What is the difference between the human genome and a pair of headphones? – Not Exactly Rocket Science : Not Exactly Rocket Science.” blogs.discovermagazine.com
- Perry Marshall. “The Mathematics of DNA.” evo2.org
- Andras Pellionisz. “News Bulletin of International HoloGenomics Society.” [Note that it links to an 8:58 min long video titled “Dr. Andras Pellionisz explains the ‘fractal genome’ ”] web.archive.org (archived from the original at www.junkdna.com)
- John W. Oller, Jr.’s channel. “Dr. Andras Pellionisz explains the “fractal genome” – YouTube.” [8:58 min long video, see from 2:47 to 6:17 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- David Pincus. “Fractal Brains: Fractal Thoughts | Psychology Today.” www.psychologytoday.com
- Wai H. Tsang’s channel. “Fractal Brain Theory Book Advert HD – YouTube.” [1:06 min long video] www.youtube.com
- A Quest For Meaning – The movie’s channel. “Bruce Lipton ‘The fractal geometry’ – YouTube.” [3:14 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Omega Institute for Holistic Studies’ channel. “Bruce H. Lipton: When You Understand a Cell, You Understand Humans – YouTube.” [3:14 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Findhorn Foundation’s channel. “Jude Currivan – ‘A Great Thought…’ – YouTube.” [24:44 min long video, see from 9:51 to 11:05 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Yitzhaq Hayut-man. “The Fractal Pattern of the Torah Bible.” israelseen.com
- Natan Slifkin. “Rationalist Judaism: Patterns in the Torah.” www.rationalistjudaism.com
- Michael Bull. “Welcome | Bible Matrix.” www.biblematrix.com.au
- The Bible Project’s channel. “How to Read the Bible: Plot – YouTube.” [5:12 min long video] www.youtube.com
- The Bible Project’s channel. “How to Read the Bible: Design Patterns – YouTube.” [6:06 min long video. Note that the patterns of water starting at the 3:18 minute mark are the same as the ones in the second (and sometimes sixth) column of my fractal periodic table of the Bible] www.youtube.com
- Isaiah Connections contributors. “Isaiah Connections – …Faith cometh by hearing and hearing by the word of God… Romans 10:17.” [Note that “today many people who study the Scriptures call the book of Isaiah a ‘miniature-Bible,’ this is for numerous reasons. For one, the book of Isaiah has 66 chapters, and the Bible has 66 books. Incredibly, every chapter of Isaiah is connected to the book it represents chronologically”] isaiahminibible.com
- Chris
Harrison. “Chris Harrison | BibleViz.” [Note that while this visualization of cross-references in the Bible may not be fractal, it still makes a beautiful “rainbow” of links] www.chrisharrison.net - Alexander Poltorak. “Sanctuary in Five Dimensions | Torah and Science.” www.quantumtorah.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Great Commandment – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Jewish ethics – Wikipedia.” [Summaries of classical rabbinic ethics section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Emergence – Wikipedia.” [Definitions section. For example, a water molecule made up of hydrogen and oxygen atoms has emergent properties that can not be predicted from the behavior of either of the two elements separately. In contrast, combining water and dirt yields a predictible resultant that can turn out to be either damp soil, mud, or dirty water depending on how much of each is used] en.wikipedia.org
- Closer To Truth’s channel. “David Chalmers – Why is Emergence Significant? – YouTube.” [12:42 min long video with host Robert Lawrence Kuhn, see from the beginning to 5:45 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Closer To Truth’s channel. “Philip Clayton – How Can Emergence Explain Reality? – YouTube.” [13:25 min long video with host Robert Lawrence Kuhn, see from 2:53 to 8:37 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Why Are We Here? documentary with Ard Louis and David Malone. “George Ellis: Strong and Weak Emergence on Vimeo.” [4:51 min long video] vimeo.com
- Tom Van Cutsem. “Session 5.” [Note near the bottom of the webpage that “you can consider the Mandelbrot set as a kind of ‘atlas’ of Julia sets, each point in the Mandelbrot fractal corresponding to a connected Julia fractal. The figure below depicts this relationship.”] soft.vub.ac.be
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mandelbrot set – Wikipedia.” [Formal definition section. Essentially, you take each point in the complex number plane and start multiplying it by itself (squaring it) and repeatedly feeding it back into the equation. Since complex numbers include an imaginary part, this means that the results usually rotate. If the results always remain near the same area instead of flying off, the original point is in the Mandelbrot set. Since this set is related to a type of stability, it can be seen as a metaphor for the God-created order in the cosmos] en.wikipedia.org
- Perry Marshall. “Communication 101: Information Theory Made REALLY SIMPLE.” evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “God and Other Minds – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Christliche Literatur-Verbreitung (CLV). “Am Anfang war die Information … – englisch.” [The English version of Werner Gitt’s In the Beginning was Information book with a free PDF download (click the “Kostenloser Download” link to the right), see pp. 79-82 for a synopsis. Incidentally, another person who wrote even earlier about the connection between code and mind was organic chemist A. E. Wilder-Smith in his 1970 book The Creation of Life: A Cybernetic Approach to Evolution] clv.de
- JesusLostChildren777’s channel. “How Information refute naturalism,Part 2 – YouTube.” [16:51 min long video from a talk by Werner Gitt called “In the Beginning was Information.” See from 10:18 to 13:22 for his definition of information although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Perry Marshall. “A New Theory of Evolution.” [Note that a comparison is made between random mutations and noise, which degrades or destroys a signal. The page also contains two video clips which are relevant] evo2.org
- Evolution 2.0 Prize by Perry Marshall. “Artificial Intelligence + Origin of Life Prize, $10 Million USD | HeroX.” [Note that $100,000 will be paid “for the initial discovery of such a code” and only “if the newly discovered process is defensibly patentable” will the full prize amount be paid. Incidentally, there was a similar $1 Million (U.S.) Origin-of-Life Prize offered from 1999 to 2018 by the Gene Emergence Project, led by David Abel, which went unclaimed] www.herox.com
- Perry Marshall. “Entries for the ‘Chemicals to Code’ Technology Prize.” evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Genetic code – Wikipedia.” [Codons section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “DNA codon table – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Inductive reasoning – Wikipedia.” [Comparison with deductive reasoning section] en.wikipedia.org
- Stephen Meyer’s channel. “Stephen Meyer: Charles Darwin’s Methods, Different Conclusion – YouTube.” [6:53 min long video. Note the statement from Henry Quastler that “the creation of new information is habitually associated with conscious activity.” Incidentally, “inference to the best explanation” is also known as abductive reasoning] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Syllogism – Wikipedia.” [Basic structure section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “General Scholium – Wikipedia.” [Scientific method argument section] en.wikipedia.org
- John R. Baumgardner and Jeremy D. Lyon. “A Linguistic Argument for God’s Existence.” [PDF from Journal of the Evangelical Theological Society Vol. 58, No. 4 (2015): pp. 771–786. Note the Einstein gulf discussed in section III.3 separates the world of sensory experiences from the world of concepts and propositions] www.etsjets.org
- Perry Marshall. “The Atheist’s Riddle, Part 2: Two Kinds of Things & The Infinite Chasm.” evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “TalkOrigins’ Misrepresentations of Werner Gitt and Information Theory.” [Note the importance of “how precisely do the transmitted symbols convey the desired meaning” versus just “how accurately can the symbols of communication be transmitted?”] evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Philosophy of information – Wikipedia.” [Shannon and Weaver section] en.wikipedia.org
- The Institute of Art and Ideas’ channel. “What Exists is Not Only Physical | George Ellis – YouTube.” [1:57 min long clip from a video called “Understanding Consciousness | Full Debate | Rupert Sheldrake, George Ellis, Amie Thomasson”] www.youtube.com
- Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics’ channel. “Neil Turok Public Lecture: The Astonishing Simplicity of Everything – YouTube.” [1 hour, 35 min, and 13 sec long video, see from 27:01 to 29:11 for a discussion of the beginning of mathematics, how numbers are abstractions, and the role of (non-physical) logic in proofs—although the entire video is interesting. For example, from 18:09 to 22:06 there is an explanation of the use of Fourier analysis to find a pattern of synchronicity hidden in the Cosmic Microwave Background known as the CMB power spectrum] www.youtube.com
- Perry Marshall. “If you can read this sentence, I can prove God exists.” [Incidentally, the argument is based on logical inference like in science rather than a rigorous mathematical proof. It also links to an hour and 56 sec long “Origin of Life” video] evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Origin of Life Video.” [An hour and 56 sec long video on the “Origin of Life: New Discoveries About DNA, God and Evolution”] evo2.org
- Cold-Case Christianity – J. Warner & Jimmy Wallace’s channel. “How the Origin of Life Points to the Existence of God – YouTube.” [14:37 min long video from a talk by J. Warner Wallace about his book “God’s Crime Scene – A Cold-Case Detective Examines the Evidence for a Divinely Created Universe,” see from 4:08 to the end although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- The Veritas Forum’s channel. “Is There Evidence of Something Beyond Nature? – YouTube.” [5:07 min long video from a talk by John Lennox called “Miracles: Is Belief in the Supernatural Irrational?” Incidentally, the name of the Nobel Prize winner who is mentioned is Roger Wolcott Sperry] www.youtube.com
- Closer To Truth’s channel. “Philip Clayton – How Should We Think About God’s Existence? – YouTube.” [7:19 min long video with host Robert Lawrence Kuhn, see from 5:34 to the end. Incidentally, the existence of codes which connect symbols and meaning as well as the logic used in error-correcting systems both seem to be “intimations of transcendence”] www.youtube.com
- Perry Marshall. “Random Mutations? Cut To The Chase” [Note that it is mathematically impossible to prove a sequence of data is random] evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Are the mutations that drive evolution random?” evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Evolution: The Untold Story, Part 1.” evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “The Exquisite Merger-Acquisitions of Mother Nature.” [Includes a 5:11 min long video with the same title] evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Darwinists Underestimate Nature. Creationists Underestimate God.” evo2.org
- Bite-sized Philosophy’s channel. “Jordan Peterson – Atheist Scientists vs Christian Fundamentalists – YouTube.” [10:14 min long video, see from 6:02 to the end although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel – Wikipedia.” [Thesis–antithesis–synthesis section. Note that Hegel did not use the “thesis–antithesis–synthesis” terminology (instead his terms for the three-step process were “abstract–negative–concrete”)] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Dialectic – Wikipedia.” [Hegelian dialectic section] en.wikipedia.org
- Seymour Garte. “Intrinsic Biochemical Intelligence | The Book of Works.” thebookofworks.com
- Perry Marshall. “Witness Bacteria Evolve in Real Time.” [Includes a 1:54 min long video titled “The Evolution of Bacteria on a ‘Mega-Plate’ Petri Dish (Kishony Lab)”] evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Bacteria evolve over a weekend.” [Includes a 1:03 min long video with the same title] evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Intelligent Bacteria: Cells are Incredibly Smart.” [Includes a 18:11 min long video of a TED-Ed talk titled “How bacteria ‘talk’ – Bonnie Bassler”] evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Alfred Russel Wallace – Wikipedia.” [Differences between Darwin and Wallace section. Note that “Wallace appeared to have envisioned natural selection as a kind of feedback mechanism that kept species and varieties adapted to their environment (now called ‘stabilizing’, as opposed to ‘directional’ selection).” Also, when “he likened ‘this principle … [to] the centrifugal governor of the steam engine, which checks and corrects any irregularities.’ . . . Wallace had ‘probably said the most powerful thing that’d been said in the 19th Century.’ ” Incidentally, the scientific method, which is being used to correct the mistaken idea that evolution is only based on random accidents, is also a feedback loop itself] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Charles Babbage – Wikipedia.” [Natural theology section. Note that “he preferred the conception of creation in which a God-given natural law dominated, removing the need for continuous ‘contrivance.’ ” Also, “Babbage put forward the thesis that God had the omnipotence and foresight to create as a divine legislator.”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Evolutionary creation – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “The Language of God – Wikipedia.” [BioLogos section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Natural genetic engineering – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Denis Noble – Wikipedia.” [Principles of Systems Biology section, see principle four (there is no privileged level of causality)] en.wikipedia.org
- Raymond Noble and Denis Noble. “Was the Watchmaker Blind? Or Was She One-Eyed?” www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mutation – Wikipedia.” [Randomness of mutations section] en.wikipedia.org
- JT898’s channel. “Richard Colling – Random Designer: Created From Chaos, To Connect With the Creator – Part 6 – YouTube.” [9:39 min long video, see from 3:45 to the end although the entire video is relevant. Note that the concept of random design is similar to adaptive mutation] www.youtube.com
- William M. Muir and David Sloan Wilson. “When the Strong Outbreed the Weak: An Interview with William Muir – This View Of Life.” thisviewoflife.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Unit of selection – Wikipedia.” [Group section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Convergent evolution – Wikipedia.” [Overview section] en.wikipedia.org
- Purposeful Universe’s channel. “The Kiwi Bird – A Convergent Evolution Example – YouTube.” [48 sec long video. Incidentally, kiwi birds look similar to and fill the same ecological niche as shrews and hedgehogs] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Chaos theory – Wikipedia.” [Sensitivity to initial conditions section] en.wikipedia.org
- Movieclips’ channel. “Jurassic Park (1993) – Chaos Theory Scene | Movieclips – YouTube.” [2 min and 18 sec long video, see from 0:20 to the end] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Attractor – Wikipedia.” [Strange attractor section] en.wikipedia.org
- puzzles and tunes’ channel. “Chaos Theory PBS – YouTube.” [57:34 min long video, see from 1:36 to 3:21 to see a strange attractor chaos game that builds a Sierpiński triangle, although the entire video is interesting. For example, from 47:58 to 52:15 there is an explanation of how brainwaves exhibit a strange attractor pattern which becomes more complex when searching for a solution] www.youtube.com
- James A. Shapiro, Denis Noble, and Raju Pookottil. “Home | The Third Way of Evolution.” www.thethirdwayofevolution.com
- James A. Shapiro. “Boston Review: Is Darwin in the Details? A Debate.” [“A Third Way” article] web.archive.org (archived from the original at bostonreview.net)
- Wikipedia contributors. “Teleological argument – Wikipedia.” [“Third way” proposal section] en.wikipedia.org
- Perry Marshall. “Evolution 2.0” evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Evolution 2.0 on CBS 6, Richmond Virginia station WTVR.” [A 5:29 min long video] evo2.org
- EES contributors. “Extended Evolutionary Synthesis – An integrative research program.” extendedevolutionarysynthesis.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Extended evolutionary synthesis – Wikipedia.” [Recent history section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Facilitated variation – Wikipedia.” [Facilitated variation and evolution section] en.wikipedia.org
- Heriot-Watt University. “Quantum observers may be entitled to their own facts.” phys.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “John Archibald Wheeler – Wikipedia.” [Participatory Anthropic Principle section] en.wikipedia.org
- PBS Space Time’s channel. “Does the Universe Create Itself? – YouTube.” [18:43 min long video, see from 10:05 to 13:30 although the earlier part of the video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Matthew Francis. “Quantum decision affects results of measurements taken earlier in time | Ars Technica.” [Note that the delayed-choice entanglement swapping gives rise to the seeming appearance of quantum retrocausality] arstechnica.com
- George Musser. “Time Entanglement Raises Quantum Mysteries | Quanta Magazine.” [Note the experiment conceived by Robert Spekkens, where the choice of measurement seems to retroactively decide which bit the photon appears to hold] www.quantamagazine.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Delayed choice quantum eraser – Wikipedia.” [Notes section, see note two from Brian Greene regarding retrocausality which explains how the experiment shows a second measurement constrains what can be said about an initial measurement] en.wikipedia.org
- University of Southampton. “Study reveals substantial evidence of holographic universe.” phys.org
- Brian Koberlein. “New Evidence for the Strange Idea that the Universe Is a Hologram.” nautil.us
- Wikipedia contributors. “Axis of evil (cosmology) – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Fermilab’s channel. “Puzzling Mysteries of the Universe – YouTube.” [11:27 min long video where the first half is about the cosmological “axis of evil,” see from the beginning to 6:35] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Inflation (cosmology) – Wikipedia.” [Criticisms section. Note that “the invoked inflaton field does not correspond to any known physical field, and that its potential energy curve seems to be an ad hoc contrivance to accommodate almost any data obtainable.” Basically, inflation seems to have been manufactured by scientists as a way to explain why the cosmic microwave background radiation of the universe is so uniform. It appears to be an attempt by members of the scientific community to uphold the Copernican principle (which means humans on the Earth are not privileged observers of the universe) that is actually worse than the often ridiculed concept of “adding epicycles” to describe elliptical orbits in the ancient Ptolemaic model of the universe] en.wikipedia.org
- Natalie Wolchover. “Using the ‘Bootstrap,’ Physicists Uncover Geometry of Theory Space | Quanta Magazine.” www.quantamagazine.org
- The Physics arXiv Blog contributors. “The Origin of Life And The Hidden Role of Quantum Criticality – The Physics arXiv Blog – Medium.” medium.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Quantum biology – Wikipedia.” [Enzymatic activity (quantum biochemistry) section] en.wikipedia.org
- Frank Trixler. “Quantum Tunnelling to the Origin and Evolution of Life.” [5. QUANTUM TUNNELLING IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY section. Note that “the key factor which enables DNA repair is electron tunnelling”] www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Wikipedia contributors. “Quantum biology – Wikipedia.” [DNA mutation section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Rate of evolution – Wikipedia.” [Fossil record section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Timeline of time measurement inventions – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Timeline of aviation – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Retrocausality – Wikipedia.” [Quantum physics section. Note that consistent with the no communication theorem, it is not possible to transmit retrocausal signals. However, this does not rule out the retrocausal collapse of a wavefunction, including one which is universal (basically a universe in a state of quantum superposition that can also be described as a virtual multiverse)] en.wikipedia.org
- Closer To Truth – Physics of the Observer’s channel. “Paul Davies – What are Observers? – YouTube.” [11:58 min long video with host Robert Lawrence Kuhn, see from 6:29 to the end although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Vienna University of Technology. “Is the universe a hologram?” [Note that “the holographic principle can also be realized in flat spaces. It is evidence for the validity of this correspondence in our universe”] phys.org
- Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology. “New math bridges holography and twistor theory.” phys.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Holographic principle – Wikipedia.” [High-level summary section] en.wikipedia.org
- World Science Festival’s channel. “What is the Holographic Principle? – YouTube.” [2:59 min long clip from a video of a 2011 World Science Festival panel discussion on the holographic principle called “A Thin Sheet of Reality: The Universe as a Hologram”] www.youtube.com
- Findhorn Foundation’s channel. “Jude Currivan – ‘A Great Thought…’ – YouTube.” [24:44 min long video, see from 13:35 to 16:51 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Seymour Garte. “Darmarckian Evolution | The Book of Works.” [Note that “the crucial difference is that mutations are very rare, accumulate slowly, and are random, while epigenetic effects can be very rapid, much more frequent, and targeted to specific genes”] thebookofworks.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Lamarckism – Wikipedia.” [Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance section] en.wikipedia.org
- Emily Singer. “How New Genes Arise from Scratch | Quanta Magazine.” www.quantamagazine.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Orphan gene – Wikipedia.” [Sources section] en.wikipedia.org
- Denis Noble. “Differential and integral views of genetics in computational systems biology | Interface Focus.” [Note Figure 3, which models a genetic buffering mechanism of the sinus node pacemaker of the heart] royalsocietypublishing.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Genetic redundancy – Wikipedia.” [Note that “the very existence of genetic buffering, and the functional redundancies required for it, presents a paradox in light of the evolutionary concepts”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Robustness (evolution) – Wikipedia.” [Mutational robustness section] en.wikipedia.org
- The Institute of Art and Ideas’ channel. “Richard Dawkins and long-time rival Denis Noble go head to head on the selfish gene | Who is right? – YouTube.” [5 min long clip from a video called “Dawkins re-examined,” see from 1:51 to 3:55] www.youtube.com
- Wikiquote contributors. “Hugo De Vries – Wikiquote.” [Note the quote that “natural selection may explain the survival of the fittest, but it cannot explain the arrival of the fittest.”] en.wikiquote.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mutation – Wikipedia.” [Randomness of mutations section. Note that “biologically important regions were found to be protected from mutations and mutations beneficial to the studied plant were found to be more likely – i.e. mutation is ‘non-random in a way that benefits the plant’ ”] en.wikipedia.org
- UC Davis. “Study challenges evolutionary theory that DNA mutations are random.” [Note that “it turns out that mutation is very non-random and it’s non-random in a way that benefits the plant. It’s a totally new way of thinking about mutation.”] phys.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Evolutionary developmental biology – Wikipedia.” [The origins of novelty section. Note the “surprising and, perhaps, counterintuitive (from a neo-Darwinian viewpoint) results of recent research in evolutionary developmental biology is that the diversity of body plans and morphology in organisms across many phyla are not necessarily reflected in diversity at the level of the sequences of genes…” as well as “novelty may arise by mutation-driven changes in gene regulation”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “DNA repair – Wikipedia.” [Evolution section. Note that “more complex organisms with more complex genomes have correspondingly more complex repair mechanisms.” This is similar to having a child’s lemonade stand not only grow into a multinational corporation with improved operating procedures (allowing it to cover all of its increasing costs such as overhead expenses like physical repairs), but also simultaneously develop better ways of making sure all of its procedures are copied correctly–such as with a xerox machine as opposed to by hand] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “DNA replication – Wikipedia.” [DNA polymerase section. Note that “these three discrimination steps enable replication fidelity of less than one mistake for every 109 nucleotides added”] en.wikipedia.org
- IDquest’s channel. “David Berlinski: Rebelious Intellectual Defies Darwinism – YouTube.” [37:41 min long video, see from 5:19 to 6:32 although the entire video is interesting. Incidentally, the principle of error minimization increases the scientific rigor of the theory of evolution although it does not approach the level of what Isaac Newton did connecting the law of gravity with planetary motion] www.youtube.com
- Rachel Thomas. “It from bit? | plus.maths.org.” plus.maths.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Digital physics – Wikipedia.” [Wheeler’s “it from bit” section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “A Universe from Nothing – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “God the Father – Wikipedia.” [In Western art section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Anima mundi – Wikipedia.” [Note that in Jewish mysticism, the all-encompassing “Supernal Wisdom” that transcends, orders, and vitalises all of creation may be apprehended by a perfect tzaddik (holy man) empowered to mitigate all division and conflict within creation. This concept is similar to that of Yeshua (Jesus)] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Cosmic Consciousness – Wikipedia.” [Similar concepts section] en.wikipedia.org
- Emerging Technology from the arXiv contributors. “Physicists Convert Information Into Energy – MIT Technology Review.” www.technologyreview.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Process theology – Wikipedia.” [Themes section. Note that “all experience (male, female, atomic, and botanical) is important and contributes to the ongoing and interrelated process of reality.” Incidentally, a concept similar to this aspect of process theology was expressed by Ibn Arabi, a Muslim scholar, mystic, poet, and philosopher who lived during the 12th and 13th centuries and who said, “God sleeps in the rock, dreams in the plant, stirs in the animal, and awakens in man”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Supernatural – Wikipedia.” [Process theology section] en.wikipedia.org
- Robert Doyle. “Information.” www.informationphilosopher.com
- Robert Doyle. “Value.” [Note that “Information philosophy replaces the difficult problem of ‘Does God exist?’ with the more tractable problem ‘Does Goodness exist?’ ”] www.informationphilosopher.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Entropy – Wikipedia.” [Philosophy and theoretical physics section. Note that “entropy is the only quantity in the physical sciences that seems to imply a particular direction of progress, sometimes called an arrow of time”] en.wikipedia.org
- BBC’s channel. “Brian Cox explains why time travels in one direction – BBC – YouTube.” [5:32 min long video. Note that physicist Brian Cox explains that entropy is the number of ways something’s constituent parts can be rearranged and not change it] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “David Hume – Wikipedia.” [Ethics section] en.wikipedia.org
- Robert Doyle. “The Cogito Model.” www.informationphilosopher.com
- Robert Doyle. “Martin Heisenberg.” www.informationphilosopher.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Interactionism (philosophy of mind) – Wikipedia.” [Problem of causal interaction section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mind–body problem – Wikipedia.” [Interactionism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “René Descartes – Wikipedia.” [Mind–body dualism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Ghost in the machine – Wikipedia.” [“Descartes’ Myth” section. Incidentally, instead of saying there is a “ghost in the machine,” it appears that spirit “matters” just as much (i.e., it is just as true to say that spirit has a physical shell around itself). More importantly, rather than there being a substance dualism where mind and body are two separate things, everything is one substance known as information and code is a third aspect of it that connects its other aspects of mind and body] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Rationalism – Wikipedia.” [Classical rationalism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Triangle of reference – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Semiotics – Wikipedia.” [Charles Sanders Peirce section. Note the triadic relationship of object, sign, and interpretant which maps to the concepts of body, code, and a mind’s interpretation of the sign. Incidentally, there is an interesting quote by John Locke earlier on the webpage that explains how science may be divided into three parts which also map to physical nature, mental reason, and communication via signs] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Charles Sanders Peirce – Wikipedia.” [Semiotic elements section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Language – Wikipedia.” [Structure section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Trinity – Wikipedia.” [Perichoresis section] en.wikipedia.org
- Perry Marshall. “Information Theory and the Trinity.” [Incidentally, Perry Marshall wrote this blog post—which includes the concept that “the communication system itself is one of the most vital fractal patterns in the universe”—after I contacted and shared my ideas about Information Trimonism with him] evo2.org
- Evolution 2.0’s channel. “Information, Communication, and the Trinitarian Concept of God – YouTube.” [5:21 min long video of Perry Marshall. Note the observation that communication is a reflection of the Trinity. Incidentally, this video inspired me to start working on what became Information Trimonism] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Aesthetics – Wikipedia.” [Computational approaches section. Note the algorithmic theory of beauty described by computer scientist Jürgen Schmidhuber who “supposes that every observer continually tries to improve the predictability and compressibility of their observations by identifying regularities like repetition, symmetry, and fractal self-similarity”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Ethics (Spinoza book) – Wikipedia.” [Structure of reality section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Double-aspect theory – Wikipedia.” [Theories section. Note that “Baruch Spinoza, who believed that Nature or God (Deus sive Natura) has infinite aspects, but that Extension and Mind are the only aspects of which we have knowledge”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Linguistic turn – Wikipedia.” [Russell and Wittgenstein section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Kenneth M. Sayre – Wikipedia.” [Philosophy of mind section. Note the “thesis that mind and matter are both reducible to an ontologically more basic “neutral” principle. The more basic principle in his account is information, in the technical sense of information theory”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Double-aspect theory – Wikipedia.” [Theories section. Note the theory by “David Chalmers, who explores a double-aspect view of information, with similarities to Kenneth Sayre’s information-based neutral monism,” although it is missing code as a third aspect] en.wikipedia.org
- Discovery Science’s channel. “Conversations with William Dembski–The Thesis of Being as Communion – YouTube.” [3:19 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Conduit metaphor – Wikipedia.” [Major framework section. Incidentally, an easier way to understand this concept is to use the three different aspects of Information Trimonism when thinking about how to send an idea to someone. First, the idea needs to be encoded into a language, which is similar to taking an object and putting it into a package. This package could have different shapes in the same way that different languages use different words for the same idea. For example, the English word “God,” Hebrew word “Elohim,” and Greek word “Theós” all refer to the “Creator and Supreme Being in the universe.” Finally, the packaged word needs to be carried by a physical medium. This could be ink, sound waves, or even electronic bits, similar to how the US Postal Service, FedEx, or UPS are different services that can be chosen to ship a package] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Karl Popper – Wikipedia.” [Popper’s three worlds section. Note that the “books, papers, paintings, symphonies, and all the products of the human mind” in World Three match the idea of an aspect of code] en.wikipedia.org
- Hans Rudolf Straub. “The theory of the three worlds (Penrose) | Hans Rudolf Straub.” [Note that “great thinkers are capable of formulating the laws of mathematics in their thoughts,” which they then encode in mathematical language] hrstraub.ch
- Wikipedia contributors. “Moving Pictures (Rush album) – Wikipedia.” [Artwork section. Note that the photographs on the cover and back of Rush’s “Moving Pictures” album make a triple entendre which matches ideas in Information Trimonism. First, the pictures which the movers are carrying are being moved physically. Second, the film crew making a motion (moving) picture of the whole scene are encoding the symbolic meaning carried in the pictures in a different format. Third, the people who are shown crying because the pictures passing by are emotionally “moving” are being affected mentally] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Holarchy – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Encyclopedia of the Philosophical Sciences – Wikipedia.” [Structure section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Turtles all the way down – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Self-reference – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mental representation – Wikipedia.” [Representational theories of mind section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Artificial neural network – Wikipedia.” [Gallery section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Hilary Putnam – Wikipedia.” [Multiple realizability section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Digital infinity – Wikipedia.” [The computational theory of mind section. Especially note the quote at the end by Steven Pinker about how (encoded) information is independent of the physical medium and is the solution to the mind–body problem] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Intentionality – Wikipedia.” [Intentionalism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Cold-Case Christianity – J. Warner & Jimmy Wallace’s channel. “How Consciousness Points to the Existence of God – YouTube.” [9:29 min long video from a talk by J. Warner Wallace about his book “God’s Crime Scene – A Cold-Case Detective Examines the Evidence for a Divinely Created Universe,” see from 4:30 to 5:35 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- drcraigvideos’ channel. “William Lane Craig vs Alex Rosenberg on Intentional States of Consciousness In the World – YouTube.” [4:43 min long video, see from 0:13 to 0:54 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Semantic externalism – Wikipedia.” [Arguments for externalism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mind–body problem – Wikipedia.” [Pre-established harmony section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Monadology – Wikipedia.” [Metaphysics section. Note that part (III) in the Summary subsection where each branch of each portion of matter “is also a similar garden or a similar pond” is essentially describing the concept of fractals. Incidentally, while we may not actually “live in the best of all possible worlds” as Leibniz claims in part (IV), we do live in a universe where it is possible to correct many different types of errors—perhaps in the most efficient way] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Leibniz’s gap – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Hard problem of consciousness – Wikipedia.” [Chalmers’ formulation section] en.wikipedia.org
- Closer To Truth’s channel. “David Chalmers – Why is Consciousness so Mysterious? – YouTube.” [11:57 min long video with host Robert Lawrence Kuhn, see from 5:38 to 9:50 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Thomas Nagel – Wikipedia.” [What is it like to be a something section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Thomas Nagel – Wikipedia.” [Natural selection and consciousness section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Knowledge argument – Wikipedia.” [Thought experiment section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Integrated information theory – Wikipedia.” [Relationship to the “hard problem of consciousness” section] en.wikipedia.org
- The Mindscience of Reality Symposium. “Federico Faggin – The Mindscience of reality.” [Incidentally, CIP stands for the cognitive, information, and physical spaces explained in the presentation abstract] mindscience.unipi.it
- Wikipedia contributors. “Systems philosophy – Wikipedia.” [Rousseau and value realism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Somatic marker hypothesis – Wikipedia.” [Hypothesis section. Incidentally, this idea was presented in the book Descartes’ Error along with the problem of trying to designate a clean border between the mind and body, which is able to be resolved with fractals. This is due to what Benoît Mandelbrot describes as their “rough or fragmented geometric shape that can be split into parts, each of which is (at least approximately) a reduced-size copy of the whole”] en.wikipedia.org
- khanacademymedicine’s channel. “Social constructionism | Society and Culture | MCAT | Khan Academy – YouTube.” [2:45 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Shannon–Weaver model – Wikipedia.” [Overview and basic components section] en.wikipedia.org
- Perry Marshall. “Gödel’s Incompleteness: The #1 Mathematical Breakthrough of the 20th Century.” evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Gödel’s incompleteness theorems – Wikipedia.” [Relationship with the liar paradox section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Symbol grounding problem – Wikipedia.” [Grounding process section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Functionalism (philosophy of mind) – Wikipedia.” [Machine-state functionalism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “John Searle – Wikipedia.” [Artificial intelligence section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Symbol grounding problem – Wikipedia.” [Searle’s Chinese room argument section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Hubert Dreyfus – Wikipedia.” [Dreyfus’ criticism of AI section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Wetware computer – Wikipedia.” [The cell as a model of wetware section] en.wikipedia.org
- cosmiccontinuum’s channel. “Secrets Of The Human Cell – Part 3 – YouTube.” [9:45 min long video, from a talk by Bruce Lipton called “As Above, So Below: An Introduction To Fractal Evolution”] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Embodied cognition – Wikipedia.” [Philosophical background section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Holography – Wikipedia.” [Basics of holography section] en.wikipedia.org
- Physics Girl’s channel. “How 3D holograms work – YouTube.” [4:18 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Allegory of the Cave – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- TED’s channel. “Your brain hallucinates your conscious reality | Anil Seth – YouTube.” [17:00 min long video, see from 7:08 to 14:13 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Light field – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Ergodic process – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- HyperPhysics by Carl R. (Rod) Nave. “Holography.” [“When a piece is the whole” section] 230nsc1.phy-astr.gsu.edu
- Wikipedia contributors. “Implicate and explicate order – Wikipedia.” [Holograms and implicate order section] en.wikipedia.org
- ThinkingAllowedTV’s channel. “Michael Talbot: Synchronicity and the Holographic Universe — Thinking Allowed w/ Jeffrey Mishlove – YouTube.” [11:19 min long video, see from the beginning to 3:37 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- LitiHolo’s channel. “Introduction To Holography – 1972 – YouTube.” [16:29 min long video. See from 0:38 to 1:38 to watch what happens when a piece is cut out of a hologram, although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Indra’s net – Wikipedia.” [Modern and Western references section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Buddhist philosophy – Wikipedia.” [Huayan section. Note that the concept of a world text “consisting of an enormous text which is as large as the universe itself” is surprisingly like the scientific holographic principle, which states that “the universe is really a hologram which is isomorphic to the information ‘inscribed’ on the surface of its boundary”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Holography – Wikipedia.” [Process section. Note the image of “a small part of an unbleached transmission hologram viewed through a microscope” showing that “the holographic information is recorded by the speckle pattern”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Turbo code – Wikipedia.” [Performance section] en.wikipedia.org
- Armin Alaghi and John P. Hayes. “Computing With Random Pulses Promises to Simplify Circuitry and Save Power – IEEE Spectrum.” [Note that the human nervous system transfers information by means of sequences of neural impulses that strongly resemble stochastic bitstreams] spectrum.ieee.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Stochastic computing – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Carlos E. Perez. “Deep Learning Machines are Holographic Memories – Intuition Machine – Medium.” [Note that “the memory capacity of a neural network seems to be highest the closer to random the weights are” and “fine tuning happens at the top.”] medium.com
- Carlos E. Perez. “Deep Learning: The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Randomness.” medium.com
- SPIE Digital Library. “Basic Principles and Applications of Holography.” [Chapter 10 of Tung H. Jeong and Lake Forest College’s book Fundamentals of Photonics (2008): pp. 381–417 in PDF format (click the “Download PDF” link to the right). See Figure 10-6 and Figure 10-7 in the “Applications of the Model” section] www.spiedigitallibrary.org
- personificationofme’s channel. “mind-blowing Seattle 3D holographic map – YouTube.” [51 sec long video] www.youtube.com
- University of Manchester. “Ancient Graphite Reveals a Quantum Surprise: Scientists Discover Hofstadter’s Butterfly” [Note that the mixing is described by a fractal Hofstadter’s Butterfly pattern, which was mentioned earlier in this webpage regarding certain electron behavior] scitechdaily.com
- Love Hate on Vimeo.” [14 sec long video of a hanging sculpture that spells two different words depending on the viewing angle] vimeo.com
- Art Insider’s channel. “Two-In-One Wire Sculptures Are Totally Mind-Bending – YouTube.” [57 sec long video of French artist Matthieu Robert-Ortis’s sculptures that show a different image depending on what angle you look at them] www.youtube.com
- Closer To Truth – Physics of the Observer’s channel. “Paul Davies – What are Observers? – YouTube.” [11:58 min long video with host Robert Lawrence Kuhn, see from the beginning to 3:38 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Natalie Wolchover. “How Space and Time Could Be a Quantum Error-Correcting Code | Quanta Magazine.” www.quantamagazine.org
- Fernando Pastawski. “Putting back the pieces of a broken hologram | Quantum Frontiers.” quantumfrontiers.com
- Beni Yoshida. “Quantum gravity from quantum error-correcting codes? | Quantum Frontiers.” quantumfrontiers.com
- S. James Gates Jr. “Symbols of Power: Adinkras and the Nature of Reality | The On Being Project.” [See the “From theoretical physics to codes” section near the bottom of the page] onbeing.org
- HiddenHalo’s channel. “James Gates Shocks Neil DeGrasse Tyson We Live In A Computer Simulation – YouTube.” [4:54 min long video from the “2011 Isaac Asimov Memorial Debate: The Theory of Everything” at the American Museum of Natural History] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Coding theory – Wikipedia.” [Neural coding section] en.wikipedia.org
- Ames Laboratory. “Researchers discover skyrmions can split like biological cells” [Note that “skyrmions can annihilate imperfections in the lattice pattern by self-splitting (similar to cell reproduction), a kind of self-healing process that has never been described before”] phys.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Centrifugal governor – Wikipedia.” [Natural selection section. Note that feedback is also important for natural selection—as first proposed by Alfred Russel Wallace (its co-discoverer along with Charles Darwin) in his quote about governors as a metaphor for the evolutionary principle] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Windmill fantail – Wikipedia.” [Incidentally, the funny “Xzibit Yo Dawg” meme can be used to describe this as “Yo dawg, I herd you like windmills, so I put a windmill on yo windmill so you can have it not mill in the wind while you mill.”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Closed-loop controller – Wikipedia.” [Closed-loop transfer function section] en.wikipedia.org
- University of California – Berkeley. “Editing brain activity with holography: Using optogenetics and holographic projection, scientists aim to implant perceptions in brain — ScienceDaily.” www.sciencedaily.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Holonomic brain theory – Wikipedia.” [Origins and development section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Holographic associative memory – Wikipedia.” [Note that while this may not be how the brain actually works, in the case of visual perception “humans can effortlessly change the focus from object to object without requiring relearning. HAM provides a computational model which can mimic this ability”] en.wikipedia.org
- ThinkingAllowedTV’s channel. “Karl Pribram: The Holographic Brain (excerpt) – A Thinking Allowed DVD with Dr. Jeffrey Mishlove – YouTube.” [5:44 min long video] www.youtube.com
- ThinkingAllowedTV’s channel. “Michael Talbot: Synchronicity and the Holographic Universe — Thinking Allowed w/ Jeffrey Mishlove – YouTube.” [11:19 min long video, see from 3:38 to the end although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Cybernetics – Wikipedia.” [In biology section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Adaptive system – Wikipedia.” [Benefit of self-adjusting systems section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Edge of chaos – Wikipedia.” [Adaptation section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Activity-dependent plasticity – Wikipedia.” [Role in learning section] en.wikipedia.org
- TEDx Talks’ channel. “After watching this, your brain will not be the same | Lara Boyd | TEDxVancouver – YouTube.” [14:24 min long video, see from 1:41 to 6:02 about neuroplasticity] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Self-organization – Wikipedia.” [Cybernetics section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mind over matter – Wikipedia.” [Origin section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Teleology – Wikipedia.” [Biology section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Watchmaker analogy – Wikipedia.” [William Paley section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Teleological argument – Wikipedia.” [Roman era section] en.wikipedia.org
- Perry Marshall. “Language and Design: Product of a Mental Process.” [See the two sections about Paley’s Design Argument near the bottom of the page] evo2.org
- Ann Gauger. “A Watch on a Heath — But What a Watch! | Evolution News.” [Note that “In fact, it’s not just a mechanism that tells you that it’s designed. It’s the information written on the face of it”] evolutionnews.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Clock – Wikipedia.” [Controller section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Clock – Wikipedia.” [Indicator section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Translation (biology) – Wikipedia.” [Basic mechanisms section] en.wikipedia.org
- ndsuvirtualcell’s channel. “Translation – YouTube.” [3:32 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Sequence hypothesis – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- IDquest’s channel. “DNA 101 How It Works and Why It’s Astounding – YouTube.” [4:21 min long video with Stephen Meyer, see from the beginning to 2:30 although the entire video is relevant. Note that it took until about 50 years ago for scientists to discover that life is something “whose seed is in itself,” which was revealed thousands of years earlier by God in Genesis 1:11] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “3-Base Periodicity Property – Wikipedia.” [History section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Specified complexity – Wikipedia.” [Criticism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Causality – Wikipedia.” [Metaphysics section. Note that “causality can be used as a prior foundation from which to construct notions of time and space”] en.wikipedia.org
- Adam Frank. “How Does The World Work: Top-Down or Bottom-Up? : 13.7: Cosmos And Culture : NPR.” www.npr.org
- Closer To Truth’s channel. “Philip Clayton – How Can Emergence Explain Reality? – YouTube.” [13:25 min long video with host Robert Lawrence Kuhn, see from 8:38 to the end although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Perry Marshall. “Atheists: Is Information Real?” evo2.org
- Stephen Meyer’s channel. “Dr. Stephen Meyer: What Kind of Information Does DNA Contain? – YouTube.” [4:36 min long video. Note that the information in DNA is meaningful or functional] www.youtube.com
- Girish Mallya. “Girish Mallya’s answer to What the difference between the Fourier Transform of an image and an image histogram? – Quora.” www.quora.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Noise (video) – Wikipedia.” [Note the image showing “noise in a CRT television”] en.wikipedia.org
- Tendero’s answer. “Why Fourier series and transform of a square wave are different? – Signal Processing Stack Exchange.” dsp.stackexchange.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “White noise – Wikipedia.” [Note the image showing “the waveform of a Gaussian white noise signal plotted on a graph”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Clock – Wikipedia.” [Oscillator section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Entropy and life – Wikipedia.” [Negative entropy section. Incidentally, the first time I learned about the laws of thermodynamics and how entropy is always increasing in the universe, I wondered how it was possible for me to be alive and sitting in a college lecture at all. I already knew that there was information encoded in DNA with the genetic code and in later engineering classes I learned about feedback loops and error correction, but I did not understand how they were connected at the time. It was years later when I started writing this book that I realized the type of information in a cell’s DNA is extremely important as it has to correct problems on multiple levels. For example, if a cell were to only store information such as sporting event scores or the latest celebrity gossip, it would not be able to manage the physical repair processes that overcome entropy let alone the ones that correct errors in its encoded information] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “What Is Life? – Wikipedia.” [Schrödinger’s “paradox” section. Note that life is able to locally reduce disorder or uncertainty by actually causing more disorder in the rest of the universe] en.wikipedia.org
- DrJamesTour’s channel. “The Science & Faith Podcast – James Tour & Brian Miller: Thermodynamics and Origin of Life – YouTube.” [1:16:03 min long video, see from 9:41 to 13:10 (which is the “The Simultaneous Necessity of Molecular Engines & Information for Life” section) although the entire video is relevant.] www.youtube.com
- TheArchangel911’s channel. “Jordan Peterson shows you a video of DNA fixing itself – YouTube.” [8:31 min long video, see from 2:15 to 3:17 although the entire video is relevant. Incidentally, the embedded TEDx animation by Drew Berry does not actually show any of the error correction in the DNA replication process, despite the title] www.youtube.com
- Perry Marshall. “Memo To PZ Myers: Damage is Random. Repair is Not.” evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Telorexia – Blind to Purpose in Nature.” evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Natural Theology or Evidences of the Existence and Attributes of the Deity – Wikipedia.” [Topics of dispute section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikiquote contributors. “Richard Dawkins – Wikiquote.” [River out of Eden (1995) section] en.wikiquote.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Error detection and correction – Wikipedia.” [History section. Note that Jewish scribes copying the Hebrew Bible formalized techniques like counting the number of letters as well as words in a line, section, book and groups of books to ensure accurate reproduction of the sacred text] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Error detection and correction – Wikipedia.” [Principles section. Incidentally, error correction uses logic, and is similar to playing the murder mystery game Clue where it is possible to figure out who the murderer is by using evidence] en.wikipedia.org
- Khan Academy Labs’ channel. “Error correction | Journey into information theory | Computer Science | Khan Academy – YouTube.” [5:24 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Hugh Henry and Daniel Dyke. “Nobel-Winning DNA Research Challenges Evolutionary Theory.” [Note that the authors say, “it seems a miracle would be necessary for all this to come together by undirected, random processes over a time span of only 1 billion years!”] www.reasons.org
- Long Story Short’s channel. “Surviving the Daily DNA Apocalypse: The Hidden Drama Inside Your Cells – YouTube.” [12:22 min long video, see from 5:43 to 7:23 although the entire video (especially the beginning) is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Frank Trixler. “Quantum Tunnelling to the Origin and Evolution of Life.” [5. QUANTUM TUNNELLING IN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY section. Note that “the key factor which enables DNA repair is electron tunnelling”] www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Wikipedia contributors. “Quantum biology – Wikipedia.” [DNA mutation section] en.wikipedia.org
- The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. “The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2015 – Press release – NobelPrize.org.” www.nobelprize.org
- The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. “The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2015 – Prize announcement – NobelPrize.org.” [Includes a 33:15 min long video of the announcement as well as a 9:26 min long video of an interview regarding the prize] www.nobelprize.org
- Vanderbilt University. “New class of DNA repair enzyme discovered — ScienceDaily.” www.sciencedaily.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “RNA world – Wikipedia.” [RNA in information storage section] en.wikipedia.org
- Seymour Garte. “RNA and the Origin of Life | The Book of Works.” [Note that “there is still no known mechanism for RNA to self-replicate”] thebookofworks.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Nothing in Biology Makes Sense Except in the Light of Evolution – Wikipedia.” [The phrase section. Note that this is the title of a famous 1973 essay by evolutionary biologist Theodosius Dobzhansky which supports the idea of an evolutionary creation] en.wikipedia.org
- Seymour Garte. “Replication (Part 2) | The Book of Works.” [Note the paradox that “accurate replication is required for evolution, and evolution is required for accurate replication”] thebookofworks.com
- Seymour Garte. “Replication and Evolution | The Book of Works.” [Note that “a smoothly continuous evolutionary path to high replication fidelity is impossible.” However, another blog post about the results of his replication fidelity paper (see https://thebookofworks.com/2020/11/17/my-latest-research-on-origin-of-life/) says that “contrary to expectation, cell populations with very low (even zero) replication fidelity can survive and evolve, although barely” and “with no replication fidelity at all, the minimum value of survival probability to avoid extinction is 95%.” Overall the paper “strongly suggests that early life could not have evolved without some dramatic jumps in the levels of both survival probability and the accuracy of cellular self-replication,” which indicates that the gradual random accidents of neo-Darwinism are not the only principle involved in the origin of life] thebookofworks.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Self-replication – Wikipedia.” [Mechanical self-replication section] en.wikipedia.org
- Perry Marshall. “Frequently Asked Questions.” [Why couldn’t DNA have evolved question] evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Self-replication – Wikipedia.” [Theory section. Note that no exceptions to John von Neumann’s “a coded representation of the replicator” have yet been achieved] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Karl Popper – Wikipedia.” [Origin and evolution of life section. Note the quotes near the middle “regarding DNA and the origin of life” which talk about the genetic code and “a disturbing riddle” plus “a really baffling circle”] en.wikipedia.org
- Closer To Truth’s channel. “Paul Davies – Gap Between Non-Life and Life – YouTube.” [10:48 min long video with host Robert Lawrence Kuhn, see from 7:06 to the end although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Marcel P. Schützenberger. “Algorithms and the Neo-Darwinian Theory of Evolution.” [PDF of a paper in the Mathematical Challenges to the Neo-Darwinian Interpretation of Evolution book from a symposium held at the Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology, April 25 and 26, 1966: pp. 73–80. Note on page 75 it says, “We can specify what it would take to have the random modification introduced so that a sizable fraction of all programs start working: it is a self-correcting mechanism which must incorporate something like a symbolic formulation of what ‘computing’ means.”] www-igm.univ-mlv.fr
- Wikipedia contributors. “DNA repair – Wikipedia.” [Mechanisms section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Hypercycle (chemistry) – Wikipedia.” [Error threshold problem section. Note that the hypercycle is actually a purely theoretical formulation. In fact, earlier in the Wikipedia page it is explained as “an abstract model of organization of self-replicating molecules connected in a cyclic, autocatalytic manner.” The article also says “we still lack the experimental demonstration of hypercycles”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Error threshold (evolution) – Wikipedia.” [Eigen’s paradox section. Note that “a number of solutions to this paradox have been proposed,” but it turns out there are problems with them. For example, the stochastic corrector model does not scale up very well. In addition, even though the size of a relaxed error threshold is larger, life still must be governed by non-random logical principles almost immediately] en.wikipedia.org
- DrJamesTour’s channel. “The Science & Faith Podcast – James Tour & Brian Miller: Thermodynamics and Origin of Life – YouTube.” [1:16:03 min long video, see from 22:40 to 26:45 in the “Chemical Selectors, Autonomy, the Problem of Fidelity, and Eigen’s Paradox” section although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Exclusive or – Wikipedia.” [Definition section. Note the diagram on the right of a binary Walsh matrix where each row “is the truth table of the variadic XOR of the arguments shown on the left,” which shows that aspects of logic are fractal. Incidentally, a Walsh matrix is used in the Hadamard transform, which is a type of Fourier transform. Also, while XOR may seem complicated, it basically is equivalent to the idea that “one of these things is not like the other,” similar to the famous Sesame Street TV show song] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “DNA repair – Wikipedia.” [Evolution section. Note that “more complex organisms with more complex genomes have correspondingly more complex repair mechanisms.” This is similar to having a child’s lemonade stand not only grow into a multinational corporation with improved operating procedures (allowing it to cover all of its increasing costs such as overhead expenses like physical repairs), but also simultaneously develop better ways of making sure all of its procedures are copied correctly–such as with a xerox machine as opposed to by hand] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Irreducible complexity – Wikipedia.” [Response of the scientific community section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Watchmaker analogy – Wikipedia.” [Contemporary usage section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Falsifiability – Wikipedia.” [The problem of induction section] en.wikipedia.org
- Clyde A. Hutchison III et al [including J. Craig Venter]. “Design and synthesis of a minimal bacterial genome.” [PDF from Science Vol. 351 Issue 6280 (25 March 2016) p.1414 to aad6253-11. Note that as shown in Fig. 6 at the bottom of page 7, despite shrinking the genome to 473 minimal genes (with an encoded size of 531 kilobase pairs), 41% of them are still required for reading and expressing genome information while 7% are still required for the preservation of genome information] cba.mit.edu
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mycoplasma laboratorium – Wikipedia.” [JCVI-syn3.0 section] en.wikipedia.org
- Seymour Garte. “My Favorite Enzyme Part 3 (Final) | The Book of Works.” [Note that “we have no idea what came before and how the present universal system evolved, since it’s this system that is the biochemical key to evolution.” Incidentally, there seems to be a connection between the physical shape of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase editing sites and the charged tRNAs containing anticodons, which means it might be possible to analyse them and derive the origin of the genetic code] thebookofworks.com
- JM Berg, JL Tymoczko, L. Stryer. “Biochemistry. 5th edition.” [29.2.3. Proofreading by Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases Increases the Fidelity of Protein Synthesis section] www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Wikipedia contributors. “Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase – Wikipedia.” [Mechanism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Perry Marshall. “ ‘Not only has Dawkins ruined science. He’s ruined atheism too.’ ” evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Yes, Richard Dawkins is Obsolete.” evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Jerry Coyne Evades Evolution 2.0.” evo2.org
- Stephen Meyer’s channel. “Stephen Meyer Critiques Richard Dawkins’s ‘Mount Improbable’ Illustration – YouTube.” [4:57 min long video. Incidentally, in order to metaphorically climb up the backside of “Mount Improbable,” the gradually sloping trail of small steps actually requires constant fixing or error correction because it is always in the process of crumbling due to the inherent instability of DNA molecules. Basically, “the floor is lava”—which is a fun way of saying that the back of the mountain would really be having constant eruptions with molten rock flowing down that makes it a lot harder to climb] www.youtube.com
- Perry Marshall. “Evolution Fist Fight at the Wistar Institute.” [Note the page also contains a 36:51 min long video of a talk titled “British Biologist Denis Noble Debunks Neo Darwinism”] evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Royal Society’s ‘New Trends in Biological Evolution’ – A Bloodless Revolution.” [Note the “real-time plasticity of plants” and how “plants in low-light environments produce offspring with large, light-sensitive leaves, but identical plants in high-light environments birth offspring with small leaves”] evo2.org
- Brian Miller. “Evolution Is Best Explained by Engineering | Evolution News.” evolutionnews.org
- Discovery Science’s channel. “Information Enigma: Where does information come from? – YouTube.” [20:59 min long video featuring Stephen Meyer, a philosoper of science, and molecular biologist Douglas Axe. See from 5:38 to 16:35 although the entire video is relevant. Incidentally, I think Axe’s work on the probability of functional proteins is the dagger (or perhaps the “murder axe”) that scientifically finishes off the version of evolution with only random accidents] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Cargo cult science – Wikipedia.” [Feynman’s speech section. Note that Richard Feynman “cautioned that to avoid becoming cargo cult scientists, researchers must avoid fooling themselves, be willing to question and doubt their own theories and their own results, and investigate possible flaws in a theory or an experiment”—something many evolutionary biologists have not done] en.wikipedia.org
- PZ Myers. “Happy Intelligent Design Day! : Pharyngula.” [Ironically, PZ Myers is actually the one who is doing cargo cult science. This is because he believes the random accidents in neo-Darwinism, which have been shown to be an empty shell, are enough to cause evolution] web.archive.org (archived from the original at scienceblogs.com)
- Leading Edge Research Group. “Fractal Evolution.” [Note that Darwin wrote, “I am conscious that I am in an utterly hopeless muddle. I cannot think that the world, as we see it, is the result of chance; and yet I cannot look at each separate thing as the result of design.”] www.fractal.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Religious views of Charles Darwin – Wikipedia.” [On the Origin of Species section. Ironically, unlike modern neo-Darwinists, Charles Darwin believed that there were designed laws (which we now know include error correcting systems) in evolution. Note in the last part of the last paragraph of the section he writes, “On the other hand I cannot anyhow be contented to view this wonderful universe & especially the nature of man, & to conclude that everything is the result of brute force. I am inclined to look at everything as resulting from designed laws, with the details, whether good or bad, left to the working out of what we may call chance. Not that this notion at all satisfies me. I feel most deeply that the whole subject is too profound for the human intellect. A dog might as well speculate on the mind of Newton.— Let each man hope & believe what he can.”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “ENCODE – Wikipedia.” [Production Phase Results section] en.wikipedia.org
- Andrew Moore. “That ‘Junk’ DNA … Is Full of Information! – Advanced Science News.” [Note the “genomic code”—a structural code that defines the shape and compaction of DNA. It is embodied in the high-GC tracts of the genome and overlaps protein coding sequences] www.advancedsciencenews.com
- Perry Marshall. “The 80/20 of ‘Junk DNA’.” evo2.org
- Perry Marshall. “Testable Hypothesis for Intelligent Design, Pt 2.” [Note that most of the predictions about “Junk DNA” being functional have come true] evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Non-coding DNA – Wikipedia.” [Junk DNA section] en.wikipedia.org
- Discovery Science’s channel. “Origin of Life Requires Information (Long Story Short, Ep. 11) – YouTube.” [14:41 min long video, see from 4:18 to 6:39 although the entire video is relevant. Note that “DNA has code to regulate the regulatory process and can even have code to regulate the regulator regulators—multiple layers of coding complexity”] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “C-value – Wikipedia.” [Variation among species section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Rubik’s Cube – Wikipedia.” [Singmaster notation section] en.wikipedia.org
- Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. “Base-pairing protects DNA from UV damage.” phys.org
- Marla Vacek Broadfoot. “DNA’s Dynamic Nature Well-Suited for Blueprint of Life | Duke Today.” today.duke.edu
- Stephen J. Freeland and Laurence D. Hurst. “The Genetic Code Is One in a Million.” [PDF from Journal of Molecular Evolution Vol. 47 (1998): pp. 238-248] www.webpages.uidaho.edu
- Brian Hayes. “Ode to the Code.” [PDF from American Scientist Vol. 92, No. 6 (Nov.-Dec. 2004): pp. 494-498] bit-player.org
- Victor A. Gusev and Dirk Schulze-Makuch. “Genetic code: Lucky chance or fundamental law of nature?” [PDF from Physics of Life Reviews Vol. 1 (2004): pp. 202–229] www.webpages.uidaho.edu
- Keith McPherson. “Error Control Coding in Biology Implies Design, Part 2 (of 5).” www.reasons.org
- Fazale Rana. “FYI: I.D. IN DNA Deciphering Design in the Genetic Code.” www.reasons.org
- Stephanie Seiler. “Scientists discover double meaning in genetic code | UW News.” www.washington.edu
- Shalev Itzkovitz and Uri Alon. “The genetic code is nearly optimal for allowing additional information within protein-coding sequences.” [PDF from Genome Research Vol. 17 (2007): pp. 405–412] genome.cshlp.org
- TheWordisalive’s channel. “DNA The Genetic Code Error Minimization Parallel Codes.” [10:00 min long video from a talk by Fazale Rana called “The Cell’s Design: How Biochemistry Reveals the Work of a Creator.” See from 6:57 to 8:46 although the entire video is relevant] www.metacafe.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Perceptual control theory – Wikipedia.” [Neuroscience section. Note the suggestion of a reorganizing process “reducing outputs that cause error and increasing those that reduce error”] en.wikipedia.org
- Duke Today Staff. “Brain’s Visual Circuits do Error Correction on the Fly | Duke Today.” today.duke.edu
- Jakob Hohwy. “The Brains Blog.” [“Is prediction error minimization all there is to the mind?” post] philosophyofbrains.com
- Kyle Hill’s channel. “Why Reality is a ‘Controlled Hallucination’ – YouTube.” [15:00 min long video, see from 6:03 to 12:02 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Predictive coding – Wikipedia.” [Active inference section. Note that it is described as a “principle of prediction error minimization”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Bayesian approaches to brain function – Wikipedia.” [Free energy section. Note the quote at the end, where “it is fairly easy to show that both perceptual inference and learning rest on a minimisation of free energy or suppression of prediction error”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Free energy principle – Wikipedia.” [Relationship to other theories section. Note that “the principle of minimum variational free energy is a principle of least action.”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “History of variational principles in physics – Wikipedia.” [Principle of least action section. Note that French mathematician Pierre Louis Maupertuis felt that “nature is thrifty in all its actions” and in the following section, Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler wrote that “since the fabric of the Universe is most perfect and is the work of a most wise Creator, nothing whatsoever takes place in the Universe in which some relation of maximum and minimum does not appear.”] en.wikipedia.org
- Sabine Hossenfelder’s channel. “The Closest We Have to a Theory of Everything – YouTube.” [13 min and 27 sec long video, see from 5:36 to 10:27 for a discussion of the principle of least action—although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Shaun Raviv. “The Genius Neuroscientist Who Might Hold the Key to True AI | WIRED.” www.wired.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Bayesian approaches to brain function – Wikipedia.” [Predictive coding section] en.wikipedia.org
- Anil Ananthaswamy. “Artificial Neural Nets Finally Yield Clues to How Brains Learn | Quanta Magazine.” [Note that “with the proper setup, predictive coding networks can converge on much the same learning gradients as backprop” and “pyramidal neurons could form the basic units of a deep learning network by doing both forward and backward computations simultaneously”] www.quantamagazine.org
- Don Monroe. “Physics – Focus: Model Suggests Link between Intelligence and Entropy.” [Note the tagline that “dynamical systems that maximize their future possibilities behave in surprisingly ‘intelligent’ ways”] physics.aps.org
- Sara Imari Walker and Paul C. W. Davies. “The algorithmic origins of life | Journal of The Royal Society Interface.” royalsocietypublishing.org
- Sara Imari Walker, Hyunju Kim, and Paul C. W. Davies. “The informational architecture of the cell | Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences.” [Note the quantification and comparison of effective information (how much the causal mechanisms of a network reduce the uncertainty about the possible prior states) and integrated information (how much the “the whole is more than the sum of its parts,” which is random)] royalsocietypublishing.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Gene regulatory network – Wikipedia.” [Structure and evolution section] en.wikipedia.org
- John Ankerberg Show’s channel. “What are gene regulatory networks, and why are they a problem for Darwin’s theory? – YouTube.” [4:24 min long clip from the series “The Case for Intelligent Design” with Dr. Stephen Meyer. Incidentally, gene regulatory networks can change, but not randomly] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Alfred Russel Wallace – Wikipedia.” [Differences between Darwin and Wallace section. Note that “Wallace appeared to have envisioned natural selection as a kind of feedback mechanism that kept species and varieties adapted to their environment (now called ‘stabilizing’, as opposed to ‘directional’ selection).” Also, when “he likened ‘this principle … [to] the centrifugal governor of the steam engine, which checks and corrects any irregularities.’ . . . Wallace had ‘probably said the most powerful thing that’d been said in the 19th Century.’ ” Incidentally, the scientific method, which is being used to correct the mistaken idea that evolution is only based on random accidents, is also a feedback loop itself] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Good regulator – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Variety (cybernetics) – Wikipedia.” [Law of requisite variety section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “W. Ross Ashby – Wikipedia.” [Variety section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Ethical regulator – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikiquote contributors. “Democritus – Wikiquote.” [Quotes section. Note that Democritus said, “strength of body is nobility only in beasts of burden, strength of character is nobility in man.” It is ironic that he talked about character, which is a non-physical moral quality, because he also famously claimed, “there are only atoms and the void.” Also ironically, he used code in the form of the Greek language to symbolically represent the non-physical thoughts in his mind] en.wikiquote.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Love – Wikipedia.” [Christianity section. Note that agape love is “charitable, selfless, altruistic, and unconditional”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “No Greater Love – Wikipedia.” [Incidentally, Jesus talked about also loving your enemies in Matthew 5:43-48] en.wikipedia.org
- Lex Clips channel. “Jordan Peterson: Meaning of Life – YouTube.” [4:15 min long video. Note that “the highest value is love and truth is its handmaiden” in his hierarchy of ideals plus the discussion about the Passion Story (of Jesus) and how we have the ability to choose how to act] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Group selection – Wikipedia.” [Multilevel selection theory section. Note the quote near the picture of a nested set of Russian matryoshka dolls which says, “in a group, selfish individuals beat altruistic individuals. But, groups of altruistic individuals beat groups of selfish individuals.” Incidentally, just above it is another quote about how “at all scales, there must be mechanisms that coordinate the right kinds of action and prevent disruptive forms of self-serving behavior at lower levels of social organization.”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Thomas Hobbes – Wikipedia.” [Leviathan section. Note that Hobbes thinks that life without government and with each person in a selfish “state of nature” would be “solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, and short.” Incidentally, note the picture of the Frontispiece of Leviathan and the giant crowned figure composed of people, which is similar to a fractal body of Christ with Jesus as the head and ultimate sovereign authority] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Flammarion engraving – Wikipedia.” [Note that the engraving shows a person discovering what lies beyond the physical world and “has been used as a metaphorical illustration of either the scientific or the mystical quests for knowledge”] en.wikipedia.org
- tmcleanful’s channel. “Jordan Peterson pulls Christianity out of Sam Harris’ reductionist hat – YouTube.” [13:26 min long video, see from 4:34 to 10:01 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Alexander Poltorak. “Meaning of Life as Taught by Bayesian Angels | Torah and Science.” www.quantumtorah.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Jacob’s Ladder – Wikipedia.” [Christianity section. Incidentally, the control principles that oppose the principle of least action (and the tendency for physical things to always fall down to a state with the lowest energy) matches what Jesus says about “the spirit is willing, but the flesh is weak.” Essentially, control principles allow a way for God’s “will to be done, on earth as it is in heaven”—although people have to consciously choose to do so at a spiritual level] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Second-order cybernetics – Wikipedia.” [Relationship to “first order” cybernetics section] en.wikipedia.org
- Danko Nikolić. “Practopoietic cycle (loop) of causation.” www.danko-nikolic.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Adaptive system – Wikipedia.” [Hierarchy of adaptations: Practopoiesis section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Strange loop – Wikipedia.” [Definitions section. Note the example of “the information flow network between DNA and enzymes through protein synthesis and DNA replication”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mirror neuron – Wikipedia.” [Human self awareness section. Incidentally, mirror neurons fire when an organism acts or observes the same action performed by another, which may lead to empathy] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Kantian ethics – Wikipedia.” [Categorical imperative section. Note at the end where it says, “…we cannot opt out of being rational agents. We owe a duty to rationality by virtue of being rational agents; therefore, rational moral principles apply to all rational agents at all times.”] en.wikipedia.org
- After Skool’s channel. “The ONE RULE for LIFE – Immanuel Kant’s Moral Philosophy – Mark Manson – YouTube.” [21:49 min long video, see from 4:45 to 8:48 although the entire video is relevant] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Aesthetics – Wikipedia.” [Computational approaches section. Note the “links between aesthetics, information processing, and information theory”] en.wikipedia.org
- Harry J. Gensler. “The Golden Rule.” [Note that in the “Golden-rule books” section near the bottom of the page it says, “My Introduction to Logic, third edition (Routledge, 2017) has a chapter that formalizes a system of ethics, leading to a proof of the golden rule in symbolic logic.” Incidentally, Harry J. Gensler is a retired professor of philosophy from Loyola University Chicago] web.archive.org (archived from the original at www.harryhiker.com)
- Wikipedia contributors. “Golden Rule – Wikipedia.” [Science and economics section. Note that “in evolution, ‘reciprocal altruism’ is seen as a distinctive advance in the capacity of human groups to survive and reproduce…”] en.wikipedia.org
- Kenneth Samples. “The 3 Transcendentals: Truth, Goodness, & Beauty.” [Note that “Christian philosophers and theologians appropriated the truth of these cosmic values as truths of general revelation but grounded them in the nature of the triune God.”] www.reasons.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Transcendentals – Wikipedia.” [Note that “The conceptual idea arose from medieval scholasticism, namely Aquinas but originated with Plato, Augustine, and Aristotle in the West”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Great chain of being – Wikipedia.” [Scala Naturae in evolution section] en.wikipedia.org
- Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy contributors. “Ancient Greek Philosophy | Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy.” [Hellenistic Thought section] iep.utm.edu
- Wikipedia contributors. “Unification of theories in physics – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Grand Unified Theory – Wikipedia.” [Proposed theories section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Theory of everything – Wikipedia.” [Conventional sequence of theories section. Incidentally, a TOE in physics would be limited to only describing particles and fields even though physicist Stephen Hawking has said, “if we do discover a theory of everything…. it would be the ultimate triumph of human reason—for then we would truly know the mind of God.” In addition, except for a few formulas like the Dirac equation and the black hole entropy equation, it may not be possible to ever completely unify the hyperbolic mathematics of relativistic physics with the Fourier transform-based math of quantum mechanics. This is similar to how the hyperbolic geometric model of holography breaks down at a limit for “thin” holograms and Fourier transform-based wavefront computations have to be used instead] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Systems philosophy – Wikipedia.” [The founding of systems philosophy section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Systems theory – Wikipedia.” [General systems research and systems inquiry section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Tektology – Wikipedia.” [Overview section] en.wikipedia.org
- Robert Doyle. “Value.” [See the “A Science of Morality?” and “An Information-based Moral Code?” sections, although the whole page is relevant] www.informationphilosopher.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Fact–value_distinction – Wikipedia.” [David Hume’s skepticism section] en.wikipedia.org
- Gordon Seidoh Worley. “Minimization of prediction error as a foundation for human values in AI alignment — LessWrong.” www.lesswrong.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Logical conjunction – Wikipedia.” [Definition section. Note the diagram on the right which is labeled “Conjunctions of the arguments on the left — The true bits form a Sierpinski triangle.” This is a fractal pattern, and similar ones occur in the truth tables of the other variadic Boolean functions] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “The Human Use of Human Beings – Wikipedia.” [Science, law, and industry section. Note that the father of cybernetics says, “machines must be ‘used for the benefit of man, for increasing his leisure and enriching his spiritual life, rather than merely for profits and the worship of the machine as a new brazen calf’ ”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Golden Rule – Wikipedia.” [Religious context section] en.wikipedia.org
- Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics’ channel. “Neil Turok Public Lecture: The Astonishing Simplicity of Everything – YouTube.” [1 hour, 35 min, and 13 sec long video, see from 29:44 to 30:28 for a discussion of logic-based mathematical proof and its connection with justice, although the entire video is interesting. For example, from 18:09 to 22:06 there is an explanation of the use of Fourier analysis to find a pattern of synchronicity hidden in the Cosmic Microwave Background known as the CMB power spectrum] www.youtube.com
- Perry Marshall. “Why Christians have Failed to Reckon with Good and Evil.” [See the information about terminology just below the video and above the transcribed text] evo2.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Omega Point – Wikipedia.” [Evolution section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Cosmic Christ – Wikipedia.” [Modern ecotheology section] en.wikipedia.org
- Leading Edge Research Group. “Fractal Evolution.” [Note in the “The Fractal Ladder” section that “in terms of simple structures, evolution is more like a ladder–a fractal ladder which takes us, ‘us’ being the material realm, into higher and higher consciousness.” In addition, later on it says that “yes, we are fractals of the Creator. This is the meaning of the idea that man is made ‘in the image’ of God. This is the message of Christ. . . .”] www.fractal.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Mathematics in the Natural Sciences – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- drcraigvideos’ channel. “God and Mathematics – YouTube.” [5:03 min long video created by philosopher and theologian Dr. William Lane Craig’s Reasonable Faith organization] www.youtube.com
- Dan Simon. “Christianity and Control Theory.” [Incidentally, there also appears to be underlying connections between Christianity and the control theory concepts of observability and controllability] web.archive.org (archived from the original at academic.csuohio.edu)
- Wikipedia contributors. “Non-overlapping magisteria – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Formal science – Wikipedia.” [Incidentally, most people are probably already familiar with the formal sciences without realizing it. They are basically the fields of technology (specifically information theory), engineering, and math. These make up three quarters of the STEM acronym, which also includes the empirical natural and social sciences] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Theological critical realism – Wikipedia.” [Note the aim of showing that “the language of science and Christian theology are similar, forming a starting point for a dialogue between the two.” For example, it is possible to conceive of a supracellular consciousness (which is what a human being actually is) being able to use scientific knowledge and laboratory equipment to take a dead cell from their body, repair it, and return it to life. This is something that would be impossible for an individual cell to do. In addition, it is also possible to conceive of using science to take DNA from a perfect individual cell, cloning it, and then putting it into all of the other cells in a body (which just so happen to be cancerous and would otherwise die). Both of these ideas parallel concepts in Christianity] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Paradigm shift – Wikipedia.” [History section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “The Demon-Haunted World – Wikipedia.” [Dragon in my garage section. Note that Carl Sagan’s example of claiming there is an unfalsifiable invisible dragon in his garage as a metaphor for religious superstition is ironically a straw man fallacy that he warns about later (see number 18 in the “Logical fallacies” section lower down on the same Wikipedia page). This is because even during Sagan’s time, Christians like A. E. Wilder-Smith were saying what actually needs to be explained is the ultimate source of the encoded signal sent by the remote control in his garage to the garage door opener. Remember that no known laws of physics can create information. What also needs to be explained nowdays is the initial origin of the error-correcting mechanism in the garage door opener that can reverse the door if it strikes a solid object (which is similar to the “built-in error-correcting machine” of science that Sagan talks about in the earlier “Themes” section)] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Psalm 82 – Wikipedia.” [Christianity section. Note that Jesus quotes part of verse 6 (“I said, ‘You are gods’ ”) in John 10:34. However, he does not quote verse 7 (“But ye shall die like men, and fall like one of the princes”) or previous verses explaining that God renders judgment among the gods because they defend the unjust and show partiality to the wicked] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Mizraim – Wikipedia.” [Note that Mizraim “is the Hebrew and Aramaic name for the land of Egypt….” and according to the Biblical account section later in the webpage, “in the Book of Exodus, it is considered the house of bondage…for by strength of hand the LORD brought you out from this place….” This is because in Jewish thought, it is a spiritual metaphor for a place of narrows where someone lives as a slave after they sin, which restricts their future choices] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Psalm 19 – Wikipedia.” [King James Version section. Note that verse 10 says the law (or instruction), testimony, statutes, and commandment(s) of the Lord are “more to be desired are they than gold” and “sweeter also than honey.” Incidentally, the Psalm also indirectly talks about three levels of reality: physical matter, information in the form of commandments which “rejoice the heart” when kept, and error correction in the form of cleansing behavioral faults—which also includes God being referred to as “my Redeemer”] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “2 Timothy 3 – Wikipedia.” [Verse 16 section, which explains how “All Scripture is God-breathed and is useful for teaching, rebuking, correcting and training in righteousness”] en.wikipedia.org
- Steven Lehar. “An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory.” [Note in the “The Optical Fourier Transform” section that a Fourier transform can be used to describe what happens when a lens projects an image so information from every point is distributed over an entire screen, similar to a hologram. At the same time, parallel rays from the entire input image are focused onto a single central point on the screen, known as the DC component or term. This can be seen as a metaphor of the spiritual relationship between believers and Jesus—who said, “… I am in my Father, and you are in me, and I am in you.”] slehar.com
- WikiArt contributors. “Calvary – Octavio Ocampo – WikiArt.org.” [Note that Jesus is fractal in the painting] www.wikiart.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Crucifixion (Corpus Hypercubus) – Wikipedia.” [Composition and meaning section. Note that while the painting is not fractal, “the union of Christ and the tesseract reflects Dalí’s opinion that the seemingly separate and incompatible concepts of science and religion can in fact coexist”] en.wikipedia.org
- The Bible Project’s channel. “How to Read the Bible: Biblical Story – YouTube.” [5:37 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “The Lion the Witch and the Wardrobe – Wikipedia.” [Religious themes section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “David Hume – Wikipedia.” [Problem of miracles section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Ninth Bridgewater Treatise – Wikipedia.” [Note that in his book on natural theology, Charles Babbage states: “It is more consistent with the attributes of the Deity to look upon miracles not as deviations from the laws assigned by the Almighty for the government of matter and of mind; but as the exact fulfilment of much more extensive laws than those we suppose to exist.” For example, Charles Babbage would not have known anything about the physics of quantum tunneling and its role in DNA repair, channel coding in information theory (which uses error-correcting codes), or the math used in control theory] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Clarke’s three laws – Wikipedia.” [The laws section. Note that the third “law” or adage states “any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from magic,” which explains why some people get confused about the possibility of miracles] en.wikipedia.org
- The Veritas Forum’s channel. “Do the Laws of Nature Preclude the Possibility of Miracles? – YouTube.” [6:25 min long video from a talk by John Lennox called “Miracles: Is Belief in the Supernatural Irrational?” See from the beginning to 4:48] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Setpoint (control system) – Wikipedia.” [Note that “the setpoint represents the reference or goal for the controlled process variable. It serves as the benchmark against which the actual process variable (PV) is continuously compared.” This is similar to the role God plays in morality, as seen in the following quote by C.S. Lewis, “my argument against God was that the universe seemed so cruel and unjust. But how had I got this idea of just and unjust? A man does not call a line crooked unless he has some idea of a straight line. What was I comparing this universe with when I called it unjust?”] en.wikipedia.org
- drcraigvideos’ channel. “The Moral Argument – YouTube.” [5:01 min long video created by philosopher and theologian Dr. William Lane Craig’s Reasonable Faith organization. Note that like a control system’s setpoint or reference signal, “God’s nature provides an objective reference point for moral values – it’s the standard against which all actions and decisions are measured”] www.youtube.com
- Lewkrr’s question. “signal processing – Fourier transform of a 2D image, and noise cancelation – Mathematics Stack Exchange.” [Note that in signal processing, the Fourier transform can be used to take a problem that is hard to solve in one domain—such as removing noise from a 2D image—and map it to a new domain where it is easy to solve using a mask. This can be seen as a metaphor for the fact that humans are sinful, but this can be solved through Jesus’ atoning death, burial, and resurrection. Incidentally, even though the example uses a mask that looks like a circle, a picture where the magnitude of the Fourier transform has high frequency noise components near the corners could actually be fixed by using masks that only let an area that looks like a cross remain] dsp.stackexchange.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Romans 1 – Wikipedia.” [Verses 19–20 section. Note that God’s invisible qualities can plainly be seen through the things he has made, such as when living things mirror the divine nature and are able to use logic in encoded instructions to heal themselves. So as the Bible says, people are without excuse] en.wikipedia.org
- LitiHolo’s channel. “What happens when you cut a hologram in half? – YouTube.” [1:38 min long video. Incidentally, it is possible to pretend that the dice on the left with one dot is the head of the statue of Jesus, while the rest of the dice represent the body of Christ part. Note that “a hologram is more like a window capturing multiple perspectives of the image captured behind it, not just one perspective like a picture”] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Holography – Wikipedia.” [Fidelity of the reconstructed beam section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Computer-generated holography – Wikipedia.” [Wavefront computation section. Incidentally, growing evidence for the universe being holographic along with information theory provides a theoretical basis for Jesus’ resurrection. This was something I had been searching for since learning about quantum tunneling while I was going to college. At the time, I wondered if it was possible for Jesus to somehow “tunnel” through death in a similar way. I did know that due to the size of the human body, it no longer acts like a quantum object because of the loss of quantum coherence as it entangles with the environment—so God must have brought Jesus back to life with another method] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Magical objects in Harry Potter – Wikipedia.” [Horcruxes section. Incidentally, holograms work in a way which is somewhat similar to the horcruxes in the Harry Potter series of books that can store a person’s soul by distributing pieces of it across different objects. Note that “as the creator’s soul is divided into progressively smaller portions, they lose more of their natural humanity and the soul becomes increasingly unstable,” which is also similar to a small piece of a hologram looking a bit fuzzier] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Jonah – Wikipedia.” [In the New Testament section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Controlled burn – Wikipedia.” [Back burning section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Antifuse – Wikipedia.” [Note that “antifuses are widely used to permanently program integrated circuits (ICs),” such as programmable read-only memory (PROMs). This means an antifuse could be used to “burn” a chip, modifing it in a way that allows it to then automatically boot up when power is supplied (a metaphor for resurrection)] en.wikipedia.org
- The Bible Project’s channel. “Holiness – YouTube.” [6:34 min long video] www.youtube.com
- Wikipedia contributors. “Abundant life – Wikipedia.” [Teachings section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Holy Spirit – Wikipedia.” [Christianity section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Sheol – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Christmas – Wikipedia.” [History section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Allegory of the long spoons – Wikipedia.” en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Theosis (Eastern Christian theology) – Wikipedia.” [Deification section] en.wikipedia.org
- Wikipedia contributors. “Corporate election – Wikipedia.” [Election is offered to all people section] en.wikipedia.org